Ricoh SP3200SF User's Guide - Page 22
Network setup, Introduction, Via network administration programs, Via the control panel - printer
 |
UPC - 026649031274
View all Ricoh SP3200SF manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 22 highlights
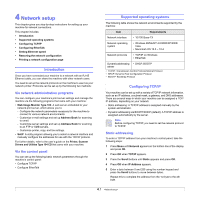
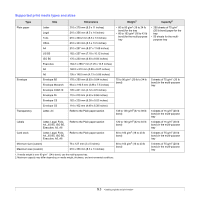
4 Network setup This chapter gives you step-by-step instructions for setting up your machine for network connections. This chapter includes: • Introduction • Supported operating systems • Configuring TCP/IP • Configuring EtherTalk • Setting Ethernet speed • Restoring the network configuration • Printing a network configuration page Introduction Once you have connected your machine to a network with an RJ-45 Ethernet cable, you can share the machine with other network users. You need to set up the network protocols on the machine to use it as your network printer. Protocols can be set up by the following two methods: Via network administration programs You can configure your machine's print server settings and manage the machine via the following programs that came with your machine: • Web Image Monitor Type 104: A web server embedded to your network print server, which allows you to: - Configure the network parameters necessary for the machine to connect to various network environments. - Customize e-mail settings and set up Address Book for scanning to email. - Customize server settings and set up Address Book for scanning to an FTP or SMB servers. - Customize printer, copy, and fax settings. • SetIP: A utility program allowing you to select a network interface and manually configure the addresses for use with the TCP/IP protocol. For further details, refer to the user's guide on the Printer, Scanner Drivers and Utilities Type 104 CD that came with your machine. Via the control panel You can set up the following basic network parameters through the machine's control panel: • Configure TCP/IP • Configure EtherTalk Supported operating systems The following table shows the network environments supported by the machine: Item Network interface Requirements • 10/100 Base-TX Network operating system • Windows 98/Me/NT 4.0/2000/XP/2003/ Vista • Macintosh OS 10.3 ~ 10.4 Network protocols • TCP/IP on Windows • EtherTalk Dynamic addressing • DHCP, BOOTP server • TCP/IP: Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol • DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol • BOOTP: Bootstrap Protocol Configuring TCP/IP Your machine can be set up with a variety of TCP/IP network information, such as an IP address, a subnet mask, a gateway, and DNS addresses. There are several ways in which your machine can be assigned a TCP/ IP address, depending on your network. • Static addressing: A TCP/IP address is assigned manually by the system administrator. • Dynamic addressing via BOOTP/DHCP (default): A TCP/IP address is assigned automatically by the server. Note Before configuring TCP/IP, you need to set the network protocol to TCP/IP. Static addressing To enter a TCP/IP address from your machine's control panel, take the following steps: 1 Press Menu until Network appears on the bottom line of the display and press OK. 2 Press OK when TCP/IP appears. 3 Press the Scroll buttons until Static appears and press OK. 4 Press OK when IP Address appears. 5 Enter a byte between 0 and 255 using the number keypad and press the Scroll buttons to move between bytes. Repeat this to complete the address from the 1st byte to the 4th byte. 4.1