Ridgid R3030 Owners Manual - Page 12
Plunge Cutting Wood Or Wall Board, Warning, Metal Cutting - saw parts
 |
View all Ridgid R3030 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 12 highlights
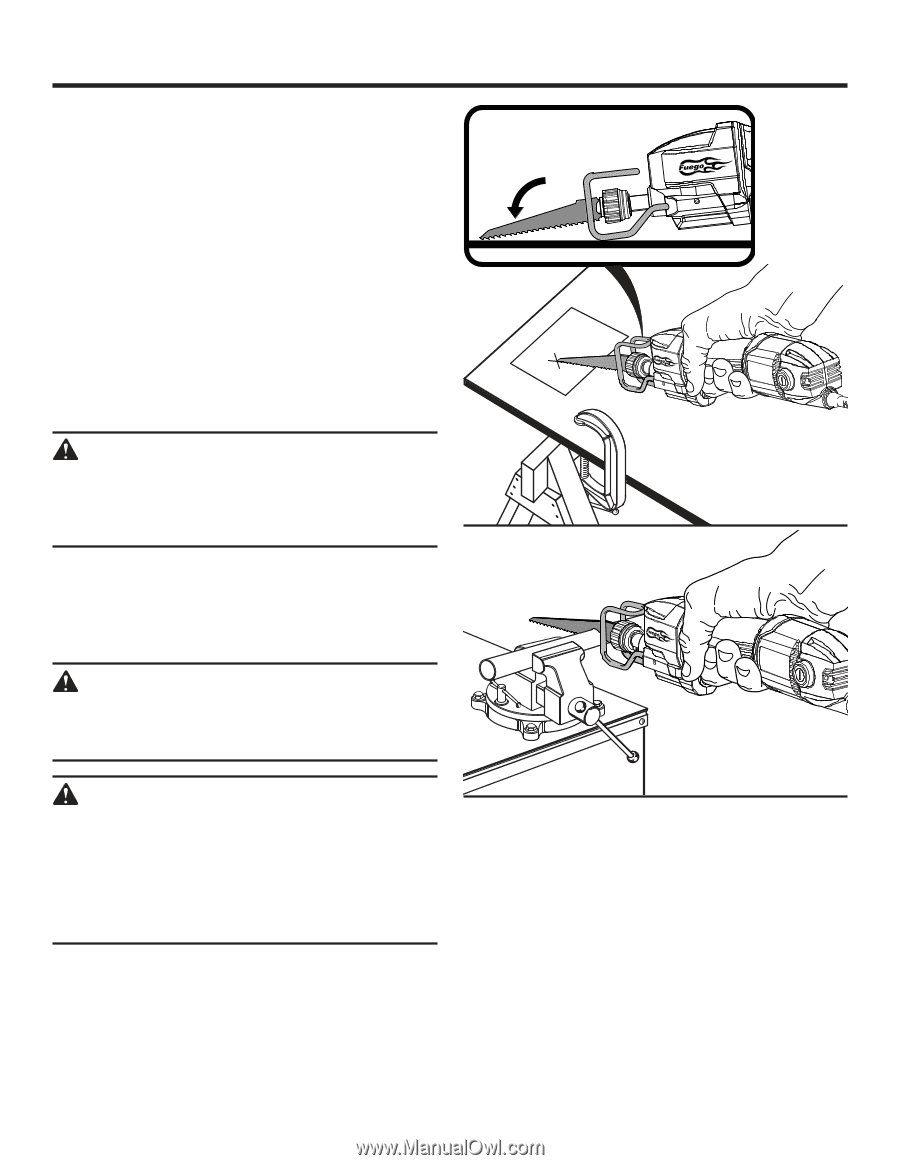
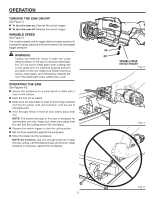
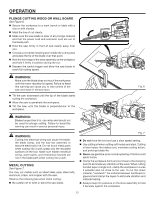
OPERATION PLUNGE CUTTING WOOD OR WALL BOARD See Figure 6. Secure the workpiece to a work bench or table with a vise or with clamps. Mark the line of cut clearly. Make sure the saw blade is clear of any foreign material and that the power cord and extension cord are out of the blade path. Hold the saw firmly in front of and clearly away from you. Choose a convenient starting point inside the cutting area and place the tip of the blade over that point. Rest the front edge of the shoe assembly on the workpiece and hold it firmly in position during the cut. Depress the switch trigger and allow the saw blade to reach full cutting speed. WARNING: Make sure the blade does not touch the workpiece until the motor reaches full speed. Failure to heed this warning can cause you to lose control of the saw and result in serious injury. Tilt the saw downward until the tip of the blade starts cutting the workpiece. Allow the saw to penetrate the workpiece. Tilt the saw until the blade is perpendicular to the workpiece. Fig. 6 WARNING: Blades longer than 6 in. can whip and should not be used for plunge cutting. Failure to heed this warning can result in serious personal injury. WARNING: Cutting into electrical wiring can cause the blade, the blade clamp, and the saw bar assembly to become electrically live. Do not touch metal parts when cutting into a wall; grasp only the insulated surfaces on the tool. Make sure hidden electrical wiring, water pipes, and mechanical hazards are not in the blade path when cutting into a wall. METAL CUTTING See Figure 7. You may cut metals such as sheet steel, pipe, steel rods, aluminum, brass, and copper with the saw. Observe the following tips when metal cutting: Be careful not to twist or bend the saw blade. Fig. 7 Do not force the tool and use a slow speed setting. Use cutting oil when cutting soft metals and steel. Cutting oil also keeps the blades cool, increases cutting action, and prolongs blade life. Never use gasoline since normal sparking of motor could ignite fumes. Clamp the workpiece firmly and cut close to the clamping point to eliminate any vibration of the work. When cutting conduit pipe or angle iron, clamp the workpiece in a vise if possible and cut close to the vise. To cut thin sheet material, "sandwich" the material between hardboard or plywood and clamp the layers to eliminate vibration and material tearing. Always keep firm pressure on the shoe assembly to hold it securely against the workpiece. 12