Seagate ST9500621SS Constellation SATA Product Manual - Page 19
Conducted noise, Note., Voltage tolerance
 |
View all Seagate ST9500621SS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 19 highlights
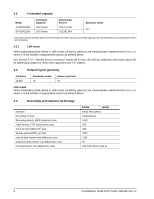
3.8.2 Conducted noise Input noise ripple is measured at the host system power supply across an equivalent 80-ohm resistive load on the +12 volt line or an equivalent 15-ohm resistive load on the +5 volt line. • Using 12-volt power, the drive is expected to operate with a maximum of 120 mV peak-to-peak square-wave injected noise at up to 10 MHz. • Using 5-volt power, the drive is expected to operate with a maximum of 100 mV peak-to-peak square-wave injected noise at up to 10 MHz. Note. Equivalent resistance is calculated by dividing the nominal voltage by the typical RMS read/write current. 3.8.3 Voltage tolerance Voltage tolerance (including noise): 5V ±5% 12V ±5% Constellation Serial ATA Product Manual, Rev. D 13

Constellation Serial ATA Product Manual, Rev. D
13
3.8.2
Conducted noise
Input noise ripple is measured at the host system power supply across an equivalent 80-ohm resistive load on
the +12 volt line or an equivalent 15-ohm resistive load on the +5 volt line.
•
Using 12-volt power, the drive is expected to operate with a maximum of 120 mV peak-to-peak square-wave
injected noise at up to 10 MHz.
•
Using 5-volt power, the drive is expected to operate with a maximum of
100 mV peak-to-peak square-wave
injected noise at up to 10 MHz.
Note.
Equivalent resistance is calculated by dividing the nominal voltage by the typical RMS read/write
current.
3.8.3
Voltage tolerance
Voltage tolerance (including noise):
5V
±5%
12V ±5%