Toshiba Satellite P500 PSPGSC-0TE00T Users Manual Canada; English - Page 102
Using the microphone, Using the TOSHIBA Face Recognition, Properties, Options, Image, Profiles
 |
View all Toshiba Satellite P500 PSPGSC-0TE00T manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 102 highlights
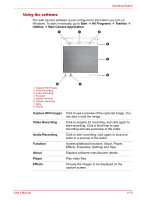
Operating Basics Properties Settings Help In the Options tab, flip or zoom the image, or set the flicker rate, night mode, and backlight compensation. In the Image tab, change the color settings. In the Profiles tab, change the lighting conditions. In the Options tab, change the tool bar position. In the Picture tab, select picture output options such as size, export file and save path. In the Video tab, choose video output settings such as frame rate, size, record compressor, and save path. In the Audio tab, change the audio device, audio compressor, audio volume and save path. Displays the help files for the software. Using the microphone Your computer has a built-in microphone that can be used to record monaural sounds with your applications. It can also be used to issue voice commands to applications that support such functions.(Built-in microphone is provided with some models) If your computer has a built-in microphone and speaker, "feedback" may be heard under certain conditions. Feedback occurs when sound from the speaker is picked up in the microphone and amplified back to the speaker, which amplifies it again to the microphone. This type of feedback occurs repeatedly and causes a very loud, highpitched noise. It is a common phenomenon that occurs in any sound system when the microphone input is output to the speaker (throughput) and the speaker volume is too loud or too close to the microphone. You can control throughput by adjusting the volume of your speaker or through the Mute function in the Master Volume panel. Refer to your Windows documentation for details on using the Master Volume panel. Using the TOSHIBA Face Recognition TOSHIBA Face Recognition uses a face verification library to verify the face data of users when they log on to Windows. This way the user can avoid having to enter a password, which makes the logon process easier. 4-14 User's Manual