Compaq ProLiant CL380 New Advanced RAID Level for Today's Larger Storage Capac - Page 2
Introduction, Smart Array Controllers
 |
View all Compaq ProLiant CL380 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 2 highlights
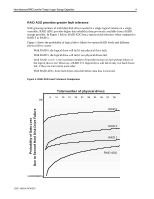
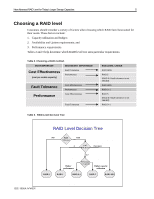
New Advanced RAID Level for Today's Larger Storage Capacities: 2 Introduction With a growing need for larger storage capacity, customers are demanding reliable ways to protect large volumes of data stored across an increasing number of disk drives. RAID technology allows a group of disk drives to be "tied" together to act like a single logical disk drive from the operating system perspective, providing increased performance and fault tolerance. Currently, Compaq offers very reliable RAID systems with the family of Smart Array Controllers that support RAID 0, 1, 0+1, and 5. For customers who wish to create large logical drives with a high number of disk drives or high capacity disk drives they need to consider the limitation of current RAID schemes. With RAID 1, it is expensive to create large volumes based upon the consumption of disk drives for mirroring. With RAID 5, it is not recommended to configure a logical drive array with greater than 14 drives due to risk of data loss. In addition, today's larger disk drive capacities may leave an array exposed to a considerable amount of risk following a single disk drive failure due to the time required to rebuild the failed drive. A second drive failure in a mirrored set in RAID 1 and any second drive failure in RAID 5 would cause an array to fail, causing data loss and downtime. With this in mind, larger capacity disk drives present new risks due to longer drive rebuild times. Compaq's new Advanced Data Guarding reduces the risk of an array failure and requires far less storage capacity overhead than RAID 1. The following table illustrates the current RAID levels used by customers, their purposes, and limitations, compared to the new advanced RAID level from Compaq: Table 1. RAID levels and functions RAID LEVEL PURPOSE RAID 0 Increased performance when no RAID protection is required. RAID 1, 0+1 Mirroring: Identical data stored on multiple drives, high fault tolerance, improved performance. RAID 5 NEW RAID ADG Distributed Data Guarding: Parity data is distributed across all drives. Protects against the failure of any one drive in an array. Provides improved performance at a minimum cost. Advanced Data Guarding: Two sets of parity data distributed across all drives. Protects against the failure of any two drives in an array. Provides high fault tolerance at a minimum implementation cost. LIMITATION No fault tolerance and highly vulnerable to failure. Requires 50% of capacity to be dedicated to fault protection. Expensive to implement across large volumes (doubling the costper-capacity). Lower fault tolerance. Not recommended for volumes greater than 14 drives. Too risky for large volumes. Lower performance than other RAID levels. 13JE-1000A-WWEN