Compaq ProLiant CL380 New Advanced RAID Level for Today's Larger Storage Capac - Page 4
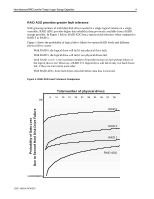
RAID ADG provides greater fault tolerance
 |
View all Compaq ProLiant CL380 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 4 highlights
New Advanced RAID Level for Today's Larger Storage Capacities: 4 RAID ADG provides greater fault tolerance With growing numbers of individual disk drives needed in a single logical volume on a single controller, RAID ADG provides higher data reliability than previously available from a RAID storage provider. In Figure 1 below, RAID ADG has a superior fault tolerance when compared to RAID 5 or RAID 1. Figure 1 shows the probability of logical drive failure for various RAID levels and different physical drive counts: • With RAID 0, the logical drive will fail if one physical drive fails. • With RAID 5, the logical drive will fail if two physical drives fail. • With RAID 1 or 0+1, the maximum number of hard drives that can fail without failure of the logical dive is n/2. However, a RAID 0+1 logical drive will fail if only two hard drives fail, if they are mirrored to each other. • With RAID ADG, three hard drives must fail before data loss is incurred. Figure 1. RAID ADG Fault Tolerance Comparison Total number of physical drives 1 1% 6 11 16 21 26 31 36 41 46 51 56 RAID 0 RAID 5 RAID 1 RAID ADG Probability of Data Loss Due to Second Hard Disk Drive Failure e 0.00000000001% 13JE-1000A-WWEN