D-Link DWL-8600AP Administration Guide - Page 68
Onfiguring, Ccess - what switch work with
 |
View all D-Link DWL-8600AP manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 68 highlights
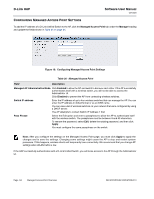
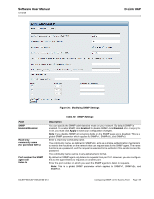
D-Link UAP Software User Manual 12/10/09 Table 29: Web Server Settings Field Description HTTPS Server Status Enable or disable access through a Secure HTTP Server (HTTPS). HTTP Server Status Enable or disable access through HTTP. This setting is independent of the HTTPS server status setting. HTTP Port Generate SSL Certificate Specify the port number for HTTP traffic (default is 80). Select this option to generate a new SSL certificate for the secure Web server. This should be done once the access point has an IP address to ensure that the common name for the certificate matches the IP address of the UAP. Generating a new SSL certificate will restart the secure Web server. The secure connection will not work until the new certificate is accepted on the browser. Note: Click Apply to apply the changes and to save the settings. If you disable the protocol you are currently using to access the AP management interface, the current connection will end and you will not be able to access the AP by using that protocol until it is enabled. CONFIGURING SNMP ON THE ACCESS POINT Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) defines a standard for recording, storing, and sharing information about network devices. SNMP facilitates network management, troubleshooting, and maintenance. The AP supports SNMP versions 1, 2, and 3. Unless specifically noted, all configuration parameters on this page apply to SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c only. Key components of any SNMP-managed network are managed devices, SNMP agents, and a management system. The agents store data about their devices in Management Information Bases (MIBs) and return this data to the SNMP manager when requested. Managed devices can be network nodes such as APs, routers, switches, bridges, hubs, servers, or printers. The UAP can function as an SNMP managed device for seamless integration into network management systems such as HP OpenView. From the SNMP page under the Services heading, you can start or stop control of SNMP agents, configure community passwords, access MIBs, and configure SNMP Trap destinations. From the pages under the SNMPv3 heading, you can manage SNMPv3 users and their security levels and define access control to the SNMP MIBs. For information about how to configure SNMPv3 views, groups, users, and targets, see "Configuring SNMPv3" on page 77. To configure SNMP, click the SNMP tab under the Services heading and update the fields described in Table 30 on page 69. Page 68 Configuring SNMP on the Access Point 34CSFP6XXUAP-SWUM100-D13