Dell PowerEdge T320 Technical Guide - Page 30
Noise ramp and descent during bootup from power off - weight
 |
View all Dell PowerEdge T320 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 30 highlights
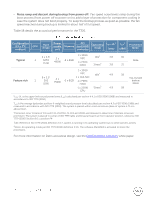
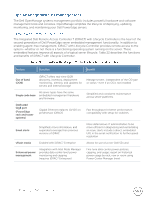
Noise ramp and descent during bootup from power off: Fan speed noise levels ramp during the boot process (from power off to power on) to add a layer of protection for component cooling in case the system does not boot properly. To keep the bootup process as quiet as possible, the fan speed reached during bootup is limited to about half of full speed. Table 18 details the acoustical performance for the T320. Configuration (23 ± 2°C ambient) CPU Hard drives Power supply unit Memory PCI card/HDD controller Operating mode LWA-UL1 (bels) LpA2 (dBA) Prominent tones3 Typical 1 4 x 3.5" SATA (7.2K) 2 x 495W 4 x 4GB 1 x 10Gb NIC 1 x PERC H310 Idle4 Stress5 3.8 3.8 30 31 None 1 x 10Gb Feature rich NIC Idle4 1 8 x 2.5" SAS (10K) 2 x 750W 1 x 1Gb NIC 6 x 8GB 1 x PERC H310 4.9 38 Yes, by hard drive at stress 1 x 225W Stress5 4.9 38 GPU 1LWA-UL is the upper limit sound power levels (LWA) calculated per section 4.4.1 of ISO 9296 (1988) and measured in accordance to ISO 7779 (2010). 2LpA is the average bystander position A-weighted sound pressure level calculated per section 4.3 of ISO 9296 (1988) and measured in accordance with ISO 7779 (2010). The system is placed within a rack enclosure (base of system is 75 cm above floor). 3Prominent tone: Criteria of D.6 and D.11 of ECMA-74 11th ed. (2010) are followed to determine if discrete tones are prominent. The system is placed in center of ISO 7779 table and binaural head is at front operator position, reference ISO 7779 (2010) Section 8.6.1, position P4. 4Idle: Reference ISO 7779 (2010) definition 3.1.7; system is running in its operating system but no other specific activity. 5Stress: An operating mode per ISO 7779 (2010) definition 3.1.6. The software MemBW4 is activated to stress the processors. For more information on Dell's acoustical design, see the Dell Enterprise Acoustics white paper.