Gateway M305 Setting up Your Windows Network - Page 69
Configuring the TCP/IP protocol, Terms you should know, Entering the IP address and subnet mask
 |
View all Gateway M305 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 69 highlights
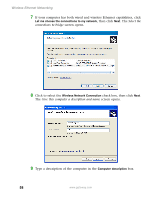
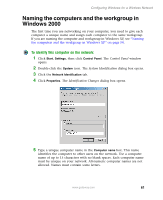
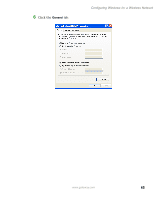
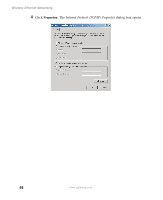
Configuring Windows for a Wireless Network Configuring the TCP/IP protocol A networking protocol is a language computers use to talk to each other. One of several available protocols must be set up on each computer you plan to use on your network. We recommend you use the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), which is widely accepted and compatible for local area networks (LANs), as well as for Internet communications. When networking is set up in Windows XP or Windows 2000, TCP/IP is automatically installed as the default protocol. Terms you should know DHCP - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) enables a router to temporarily assign an IP address to a computer on the network. IP Address - Internet Protocol (IP) address is a number that uniquely identifies a computer on the network. Subnet Mask - This number identifies what subnetwork the computer is located on. This number will be the same on all computers on a home network. Entering the IP address and subnet mask on each computer In order to use the TCP/IP protocol on each computer, you must either set the protocol to "Obtain an IP address from a DHCP server" or make the IP address settings manually. If you use a wireless access point router that can act as the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server, you can select "Obtain an IP address from a DHCP server." Or if you require a static IP address (one that does not change), you must set the IP address manually. This means that you need to enter an IP address and a subnet mask. If you are using Windows XP, go to "Entering the IP address and subnet mask in Windows XP" on page 64. If you are using Windows 2000, go to "Entering the IP address and subnet mask in Windows 2000" on page 67. www.gateway.com 63