HP 3000 HP StorageWorks 3000/5000 Enterprise Virtual Array connectivity 4.1A f - Page 9
Logical Volume Manager, Overloaded EVA con, gurations, High-availability environment recommendations - ups
 |
UPC - 829160972251
View all HP 3000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 9 highlights
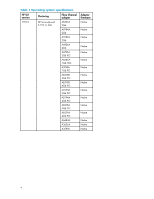
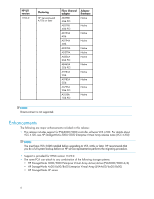
Logical Volume Manager Before you create snapshots or snapclones of a device that is managed by Logical Volume Manager (LVM), be sure to properly configure LVM. After creating a snapshot or snapclone of a physical volume, always run vgchgid(1M) to break the association between the volume group and the snapshot or snapclone. Otherwise, snapshots or snapclones appear to LVM as an alternate path to the original physical volume. This can cause data corruption if the snapshot or snapclone is added later to the volume group using vgextent(1M), vgimport(1M), or vgscan(1M). When a path to a device managed by LVM becomes unavailable because of a controller, path link, switch, or HBA failure, I/O requests can be delayed for up to one minute after the failure. As a result, the responsiveness of mirrored logical volumes may be affected briefly. When a physical volume becomes unavailable, applications may experience a delay while an I/O request to that physical volume times out. By default, this delay takes 30 seconds, but you can change the timeout value using the pvchange(1M) command. For a read, LVM selects another mirror and requests I/O again. For a write, LVM records the error and continues the write operation if the data has been written to at least one mirror. In either case, with Secure Path installed, this initial timeout can take up to one minute longer. After initial timeout, LVM stores the physical volume status as unavailable, and subsequent I/O requests are not delayed. Overloaded EVA configurations If multiple servers are overloading an EVA, the boot or reboot of one of the servers may time out. If the combined delayed access to EVA LUNs exceeds 10 minutes, the boot does not complete. To avoid this situation, restart the boot process and reduce the EVA load. CAUTION: Persistent EVA overload may indicate an overloaded configuration, and additional array host port resources may be required to match the configuration to the actual workload. Consult your HP account or service representative for help to properly configure the EVA for your newly designed or existing configuration. High-availability environment recommendations In high-availability environments with heavy I/O loads, you may experience I/O timeout conditions. If I/O time outs occur, HP recommends that you use the pvchange command to increase the IO_timeout value from the default value of 30 seconds to no more than 60 seconds. Under heavy I/O load conditions, the increased IO_timeout value allows for longer I/O completion times and LUN access delays if a controller failover occurs. NOTE: Ensure that you have HP ServiceGuard configured properly. For details, see the following website: http://docs.hp.com/hpux/ha/index.html#ServiceGuard Selecting the management appliance The menu for selecting the management appliance does not work consistently. Use the following command to access the user interface for SSSU: # gsssu In the command text box, enter an SSSU command; for example: select manager ip_address username=xxxx password=xxxx HP StorageWorks 3000/5000 Enterprise Virtual Array connectivity 4.1A for HP-UX release notes 9