HP ProLiant 800 SMART-2DH Array Controller Reference Guide - Page 140
Distributed Data Guarding RAID 5, Distributed Data Guarding distributes the redundant data [P]
 |
View all HP ProLiant 800 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 140 highlights
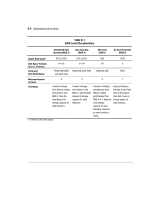
D-7 Distributed Data Guarding (RAID 5) Distributed data guarding, also called RAID 5, stores parity data across all the drives in the array. Spreading the parity across all the drives allows more simultaneous read operations and higher performance than data guarding (RAID 4). If a drive fails, the controller uses the parity data and the data on the remaining drives to reconstruct data from the failed drive. This allows the system to continue operating with a slightly reduced performance until you replace the failed drive. Distributed data guarding requires an array with a minimum of three physical drives and allows a maximum of 14 drives. Therefore, in an array containing three physical drives, distributed data guarding uses only 33 percent of the total logical drive storage capacity for fault tolerance, while a 14-drive configuration uses only 7 percent. DATA DATA DATA DATA P P P P P P P P P P = Parity WAR2-053.AI, 9-3.EPS Figure D-5. Distributed Data Guarding distributes the redundant data [P] throughout the physical drives SMART-2DH Array Controller Reference Guide Writer: Pamela King Project: SMART-2DH Array Controller Reference Guide Comments: 295469-002 File Name: K-APPD.DOC Last Saved On: 2/27/98 12:06 PM COMPAQ CONFIDENTIAL - NEED TO KNOW REQUIRED