HP ProLiant DL288 HP Advanced Memory Error Detection Technology - Page 5
HP Advanced Memory Error Detection Technology - proliant dl580
 |
View all HP ProLiant DL288 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 5 highlights
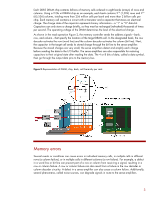
Maximum server memory capacity is also increasing to meet the demands of HPC and virtualization. For example, an HP ProLiant DL580 G7 server fully populated with 32 GB DIMMs contains 2 TB of system memory, which translates to 18 trillion memory cells. DRAM technology is changing Memory manufacturers increase DIMM storage capacity by decreasing DRAM feature size (increasing chip density). As DRAM cells become smaller, manufacturers lower the operating voltage to increase the memory speed and decrease power use. Memory manufacturers have lowered the operating voltage for standard DIMMs from 2.5 V, to 1.8 V, to 1.5 V and eventually 1.25 V. Smaller feature sizes and higher operating frequencies equate to fewer stored charges in the capacitors. This smaller number of stored charges reduces tolerance to noise sources and makes it more difficult for sense amplifiers to interpret the bit value of a capacitor‟s charge accurately. Also, reducing the number of stored charges makes it easier to change the state of a cell. This combined with higher bit density, increases the number of bits that may be affected by an ionizing event, such as an alpha particle. HP Advanced Memory Error Detection Technology Because of higher memory error frequency, some server administrators are unnecessarily shutting down servers to replace DIMMs that experience correctable errors. The best way to prevent unnecessary DIMM replacements is to filter out superfluous errors and identify critical errors that can lead to a shutdown. That‟s the goal of HP Advanced Memory Error Detection Technology. Enhancements The HP Advanced Memory Error Detection Technology algorithm analyzes multiple parameters of correctable memory error events and intelligently detects when the system is at increased probability of a non-recoverable, uncorrectable memory error condition. The algorithm performs calculations on 4-bit and 8-bit symbols instead of analyzing individual bits. It tracks multiple parameters of correctable memory errors and, after considering several properties of the DIMM, it decides when to notify the administrator to replace the DIMM. The algorithm does not prematurely alert customers to replace DIMMs based on single-bit errors because they negligibly increase the probability of an uncorrectable error. The algorithm considers unique parameters of correctable memory errors for x8 DIMMs as compared to x4 DIMMs. This is because advanced memory-correction control technologies cannot protect these DIMMs against a complete DRAM chip failure. The algorithm also detects bank failures for x4 or x8 DIMMs because these failures may increase the probability of an uncorrectable memory error. The HP iLO3 management processor sends an alert to the server‟s administrator when a DIMM exceeds a predefined threshold for correctable memory errors or experiences an uncorrectable memory error. The administrator can view a log of correctable and uncorrectable memory error events through the Integrated Management Log (IML) as shown in Figures 3A and 3B. The administrator can access the IML using a supported browser, even when the server is off. The administrator‟s ability to view the event log when the server is off can be beneficial when troubleshooting remote host server problems. 5