HP Vectra 486N and NI D27xxA hp business pcs, basic procedure to configure and - Page 6
Gateway, Subnet mask
 |
View all HP Vectra 486N and NI D27xxA manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 6 highlights
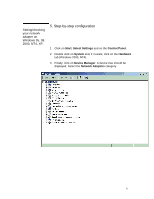
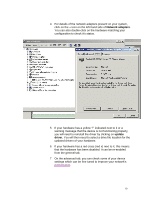
Gateway: this is a router that will locate a route to your destination on the network. This has no use on a local area network with no need to access the Internet or a remote PC (that doesn't belong to the same subnet, for example, if the distance is greater than 100m). This router is also helpful if you need to isolate some subnetworks within your network. Subnet mask: this allows you to define which IP addresses should be considered in your sub-network and which ones should not pass through the gateway. Two PCs belonging to the same sub-network do not require an external server (such as DNS or Gateways) to exchange data. Subnet masks work by "bitwise" and a mask. For example, PC A's IP address is 192.168.1.1; PC B's IP address is 192.168.0.127; PC C's IP address is 192.168.3.1 If PC A's subnet is set to 255.255.254.0, then PC B is part of A's sub-network: 192.168.1.1 and 255.255.254.0 = 192.168.0.0 192.168.0.127 and 255.255.254.0 = 192.168.0.0 Both are equal so PC A will consider PC B is part of the same sub-network. However, PC C is not part of the sub-network: 192.168.3.1 and 255.255.254.0 = 192.168.2.0 A subnet mask cannot be defined. If the mask is converted into one binary number, there must only be a transition from 1 to 0 and no transition from 0 to 1 For example, 255.255.254.0 = 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1110 0000 0000 is correct 255.0.255.255 = 1111 1111 0000 0000 1111 1111 1111 1111 is incorrect as there is a transition from 0 to 1 after a transition from 1 to 0. How do I check these settings? 6