HP Visualize J5000 HP Visualize B1000, C3000, J5000 Workstation Memory Subsyst - Page 4
New Scheduling Algorithms, New Board and DIMM Designs
 |
View all HP Visualize J5000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 4 highlights
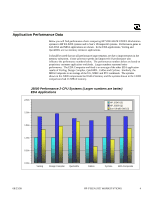
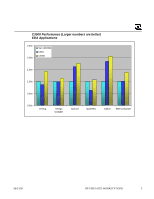
New Scheduling Algorithms Another important design feature of the HP VISUALIZE UNIX® Workstation memory system is the use of performance enhancing scheduling algorithms. One key feature of the HP VISUALIZE UNIX® Workstation systems that allows more advanced scheduling algorithms to be used is the use of open pages. With the multiple internal banks of SDRAMs it became advantageous to leave memory pages open. In leaving memory pages open, the standard DRAM sequence of activate -> column access -> precharge (close an open page) is rearranged to be precharge (close an open page) -> activate -> column access. By leaving pages open and subsequently getting a read or write command to the same page, the precharge and activate parts of the SDRAM sequence can be avoided. The use of open pages can thus improve overall busy system memory latency. In the HP PA8200 systems pages were not left open once they were accessed. Another improvement to the HP VISUALIZE UNIX® Workstation memory subsystem is the use of out of order read returns. A good example of how out of order read returns are used is the reordering of read commands based on whether the read is to an open or closed page. If two reads are waiting to be issued, the first to a closed page and the second to an open page, HP VISUALIZE UNIX® Workstation systems will reorder the reads to allow the read to the open page to execute first, or to be issued "out of order." The HP PA-8200 systems did not use out of order read returns. As explained in the open page discussion above, this improves the busy system memory latency of the HP VISUALIZE UNIX® Workstation systems. The HP VISUALIZE UNIX® Workstation systems also use a larger memory transaction queue. The larger queue is beneficial in that it allows a greater number of transactions to be prioritized. This feature couples nicely with the use of out of order read returns. With a larger transaction queue, the chance of finding a read or a write to an open page is much greater. The HP PA-8200 systems had a much smaller memory transaction queue than that of the HP VISUALIZE UNIX® Workstation systems. All of the scheduling features mentioned above contribute to the improved performance of the HP VISUALIZE UNIX® Workstation memory subsystem. New Board and DIMM Designs A key feature in the improved performance of the HP VISUALIZE UNIX® Workstation memory subsystem is the operation of standard PC100 SDRAMs at 120Mhz, as opposed to their standard operation at 100MHz. The memory subsystem is able to operate at this frequency due to a novel clocking scheme that essentially eliminates clock skew from the system's DRAM timing equations. Being able to operate the memory subsystem at this increased frequency greatly improved the performance of the HP VISUALIZE UNIX® Workstation systems. 08/23/99 HP VISUALIZE WORKSTATIONS 3