Intel Q9450 Design Guidelines - Page 30
Processor, Heatsink
 |
UPC - 735858198493
View all Intel Q9450 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 30 highlights
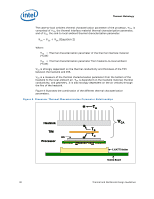
Thermal Metrology The case-to-local ambient thermal characterization parameter of the processor, CA, is comprised of CS, the thermal interface material thermal characterization parameter, and of SA, the sink-to-local ambient thermal characterization parameter: CA = CS + SA (Equation 2) Where: CS = Thermal characterization parameter of the thermal interface material (°C/W) SA = Thermal characterization parameter from heatsink-to-local ambient (°C/W) CS is strongly dependent on the thermal conductivity and thickness of the TIM between the heatsink and IHS. SA is a measure of the thermal characterization parameter from the bottom of the heatsink to the local ambient air. SA is dependent on the heatsink material, thermal conductivity, and geometry. It is also strongly dependent on the air velocity through the fins of the heatsink. Figure 4 illustrates the combination of the different thermal characterization parameters. Figure 4. Processor Thermal Characterization Parameter Relationships TA Heatsink TIM IHS Processor CA TS TC LGA775 Socket System Board 30 Thermal and Mechanical Design Guidelines