Netgear DGFV338 QoS configuration for DGFV338 - Page 2
What is Type-of-Service ToS? - qos
 |
View all Netgear DGFV338 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 2 highlights
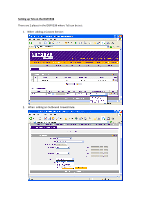
What is Type-of-Service (ToS)? ToS is an IP QoS (quality-of-service) mechanism, which uses certain bits in the IP header to indicate to network devices how packets should be treated. It is up to each network device that a packet passes through to know how to respond to the ToS bits, and if a device is not ToS-capable then the bits are simply ignored and all packets are treated in the same way. The DGFV338 complies with RFC1349, which defines 5 types of service: 1. Normal -Service 2. Minimize-Cost 3. Maximize-Reliability 4. Maximize-Throughput 5. Minimize-Delay Earlier versions of ToS only defined 4 types of service, they did not include "Minimize-Cost". The "Minimize-Cost" ToS attempts to minimize the financial cost of passing traffic, not to be confused with normal IP routing protocols which try to route packets based on minimum "Hops" or "Metrics", often referred to as "Costs". Most QoS mechanisms, including ToS, essentially consist of a number of queues of different priority that feed packets out through the physical ports of a networking device. The network device looks at the ToS bits, and places the packet in the most appropriate queue.