Panasonic AG-HMX100 3D Production Post White Paper - Page 6
Check As You Go, Post Processing
 |
View all Panasonic AG-HMX100 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 6 highlights
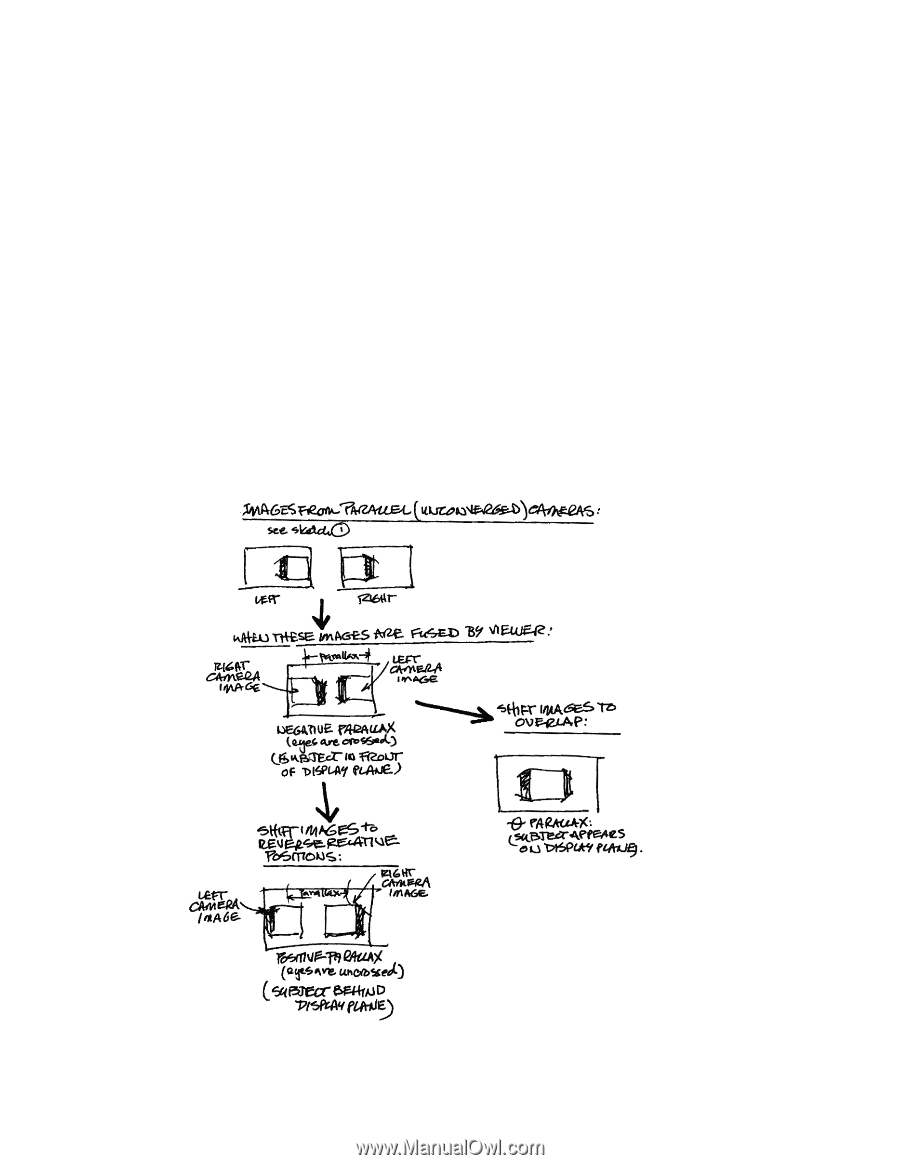
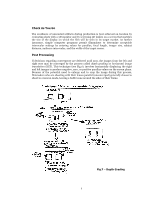
Check As You Go The avoidance of unwanted artifacts during production is best achieved on location by evaluating shots with a 3D monitor and by screening 3D dailies on a screen that matches the size of the display on which the film will be seen in its target market. As further insurance, simple computer programs permit filmmakers to determine acceptable interocular settings by entering values for parallax, focal length, imager size, subject distance, audience interocular, and the width of the target screen. Post Processing If decisions regarding convergence are deferred until post, the images from the left and right eyes may be converged by the process called depth grading or horizontal image translation (HIT). This technique (see Fig.7), involves horizontally displacing the right and left images to produce negative, zero, or positive parallax values on the screen plane. Because of the potential need to enlarge and to crop the image during this process, filmmakers who are shooting with their lenses parallel (unconverged) generally choose to shoot in overscan mode, leaving a buffer zone around the sides of their frame. Fig.7 - Depth Grading 6