Ricoh Aficio MP 2851 Security Target - Page 40
Hierarchical to, No other components., Dependencies, FDP_ACC.1 Subset access control, FMT_MSA.3
 |
View all Ricoh Aficio MP 2851 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 40 highlights
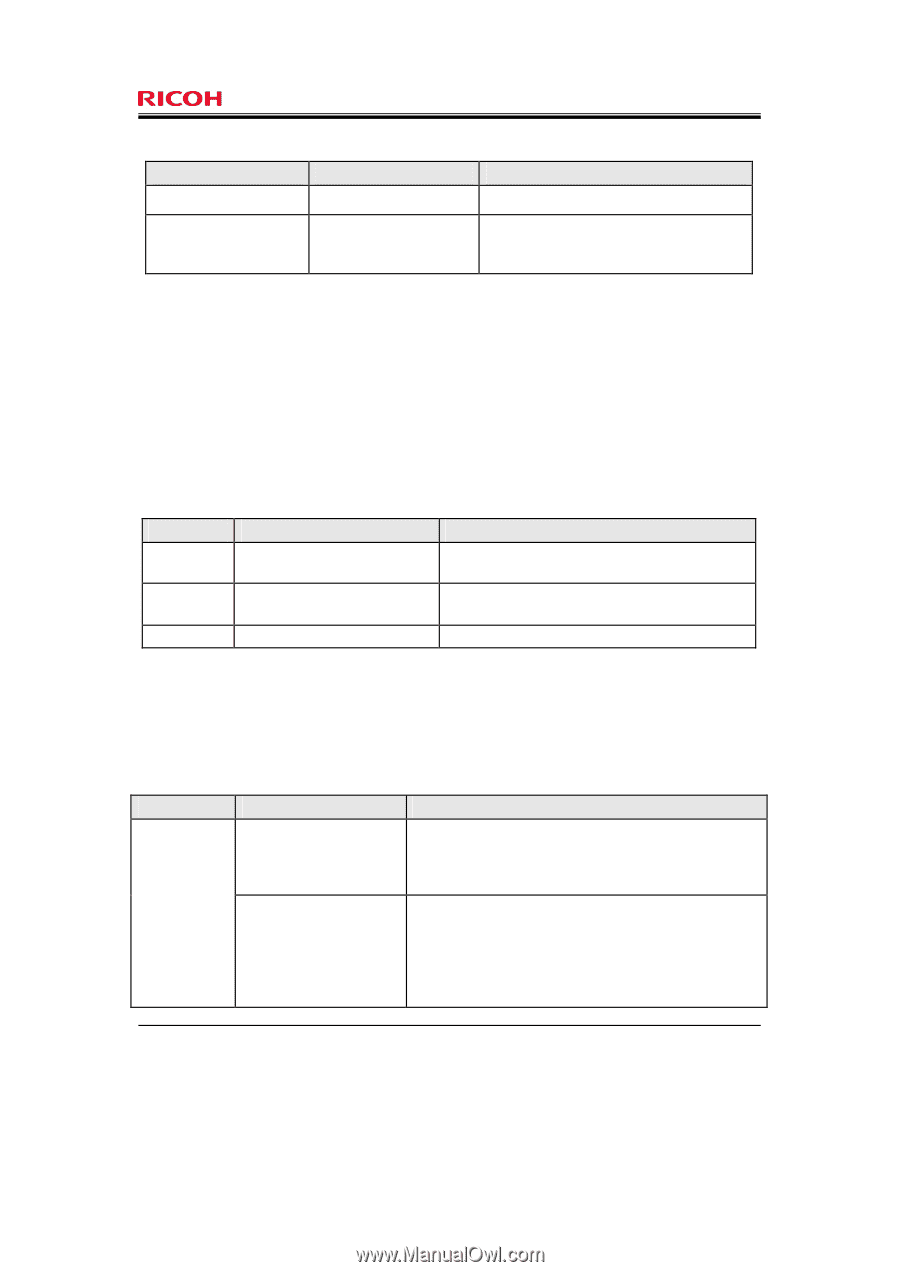
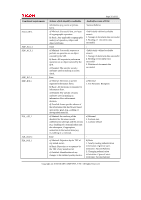
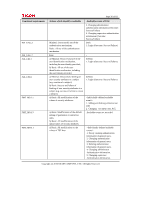
Page 40 of 81 Table 7: List of subjects, objects, and operations among subjects and objects Subjects Administrator process General user process Objects Document data Document data Operations among subjects and objects Deleting document data Storing document data Reading document data Deleting document data FDP_ACF.1 Security attribute based access control Hierarchical to: No other components. Dependencies: FDP_ACC.1 Subset access control FMT_MSA.3 Static attribute initialisation. FDP_ACF.1.1 The TSF shall enforce the [assignment: MFP access control SFP] to objects based on the following: [assignment: subjects or objects, and their corresponding security attributes shown Table 8]. Table 8: Subjects, objects and security attributes Types Subject Subject Object Subjects or objects Administrator process General user process Document data Security attributes - Administrator IDs - Administrator roles - General user ID - Document data default ACL - Document data ACL FDP_ACF.1.2 The TSF shall enforce the following rules to determine if an operation among controlled subjects and controlled objects is allowed: [assignment: rules governing subject operations on objects and access to the operations shown in Table 9]. Table 9: Rules governing access Subject General user process Operations on objects Storing document data Reading document data Rules governing access General users can store document data. When the document data is stored, the document data default ACL associated with the general user process is copied to the document data ACL associated with the document data. A general user process has permission to read document data if the general user ID associated with the general user process matches either the document file owner ID or the document file user ID in the document data ACL associated with the document data, and if the matched ID has viewing, editing, editing/deleting, or full control permission. Copyright (c) 2010 RICOH COMPANY, LTD. All Rights Reserved.