ZyXEL UAG715 User Guide - Page 104
Types of Interfaces
 |
View all ZyXEL UAG715 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 104 highlights
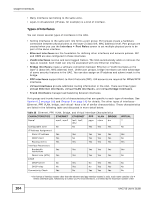
Chapter 8 Interfaces • Many interfaces can belong to the same zone. • Layer-3 virtualization (IP alias, for example) is a kind of interface. Types of Interfaces You can create several types of interfaces in the UAG. • Setting interfaces to the same port role forms a port group. Port groups create a hardware connection between physical ports at the layer-2 (data link, MAC address) level. Port groups are created when you use the Interface > Port Roles screen to set multiple physical ports to be part of the same interface. • Ethernet interfaces are the foundation for defining other interfaces and network policies. RIP and OSPF are also configured in these interfaces. • VLAN interfaces receive and send tagged frames. The UAG automatically adds or removes the tags as needed. Each VLAN can only be associated with one Ethernet interface. • Bridge interfaces create a software connection between Ethernet or VLAN interfaces at the layer-2 (data link, MAC address) level. Unlike port groups, bridge interfaces can take advantage of some security features in the UAG. You can also assign an IP address and subnet mask to the bridge. • PPP interfaces support Point-to-Point Protocols (PPP). ISP accounts are required for PPPoE/PPTP interfaces. • Virtual interfaces provide additional routing information in the UAG. There are three types: virtual Ethernet interfaces, virtual VLAN interfaces, and virtual bridge interfaces. • Trunk interfaces manage load balancing between interfaces. Port groups and trunks have a lot of characteristics that are specific to each type of interface. See Section 8.2 on page 106 and Chapter 9 on page 143 for details. The other types of interfaces-Ethernet, PPP, VLAN, bridge, and virtual--have a lot of similar characteristics. These characteristics are listed in the following table and discussed in more detail below. Table 38 Ethernet, PPP, VLAN, Bridge, and Virtual Interface Characteristics CHARACTERISTICS ETHERNET ETHERNET PPP VLAN BRIDGE Name* wan1, wan2 lan1, lan2, dmz pppx vlanx brx Configurable Zone No No Yes Yes Yes IP Address Assignment Static IP address Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes DHCP client Yes No Yes Yes Yes Routing metric Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Interface Parameters Bandwidth Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes restrictions Packet size (MTU) Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes DHCP DHCP server No Yes No Yes Yes DHCP relay No Yes No Yes Yes Connectivity Check Yes No Yes Yes Yes VIRTUAL ** No Yes No Yes Yes No No No No - * The format of interface names other than the Ethernet and ppp interface names is strict. Each name consists of 2-4 letters (interface type), followed by a number (x). For most interfaces, x is limited by the maximum number of the 104 UAG715 User's Guide