ASRock A620M Pro RS RAID Installation Guide - Page 3
RAID 1 Data Mirroring, RAID 5 Block Striping with Distributed Parity
 |
View all ASRock A620M Pro RS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 3 highlights
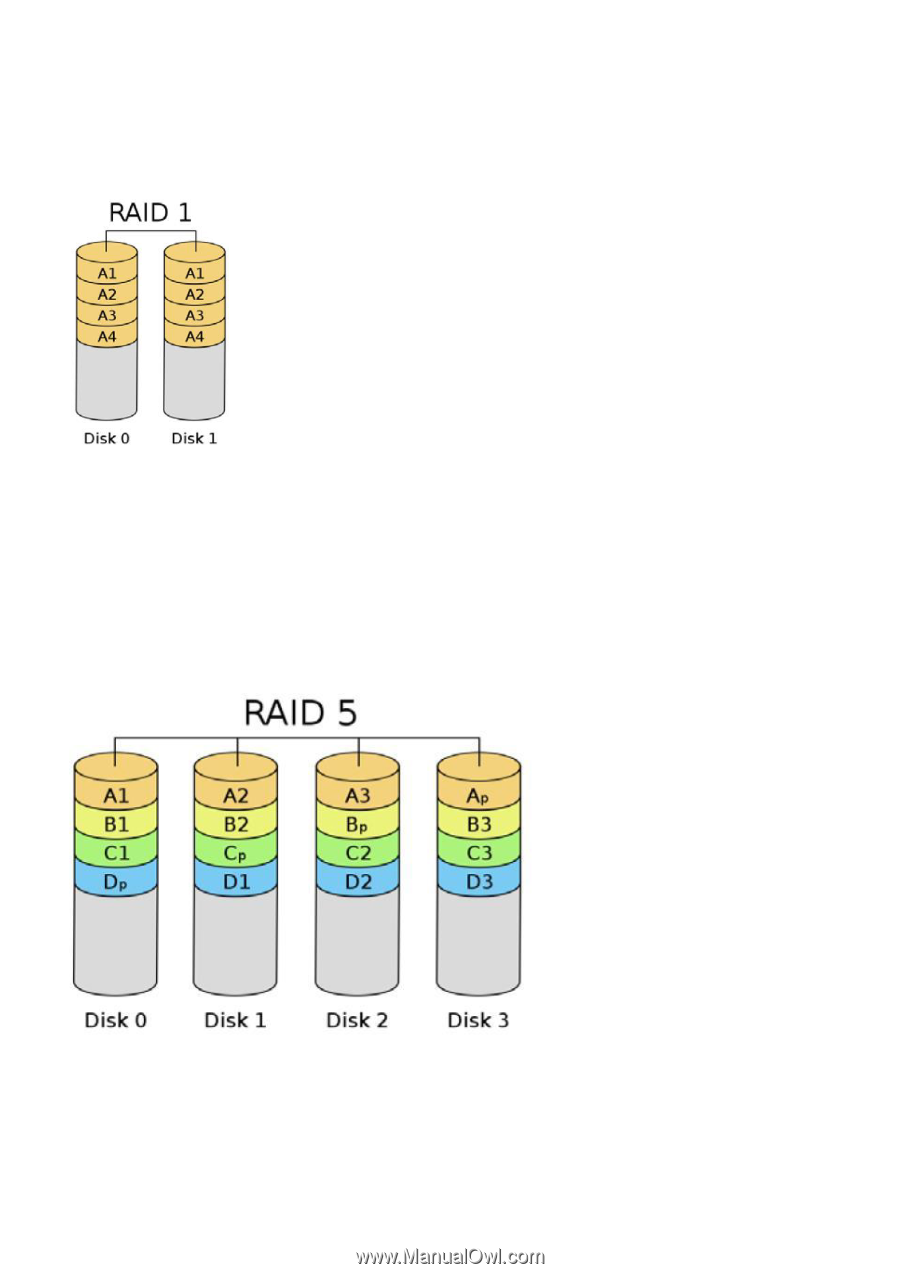
RAID 1 (Data Mirroring) RAID 1 is called data mirroring that copies and maintains an identical image of data from one drive to a second drive. It provides data protection and increases fault tolerance to the entire system since the disk array management software will direct all applications to the surviving drive as it contains a complete copy of the data in the other drive if one drive fails.3 RAID 5 (Block Striping with Distributed Parity) RAID 5 stripes data and distributes parity information across the physical drives along with the data blocks. This organization increases performance by accessing multiple physical drives simultaneously for each operation, as well as fault tolerance by providing parity data. In the event of a physical drive failure, data can be re-calculated by the RAID system based on the remaining data and the parity information. RAID 5 makes efficient use of hard drives and is the most versatile RAID Level. It works well for file, database, application and web servers. 3