Asus L2E L2E User Manual English Edition - Page 18
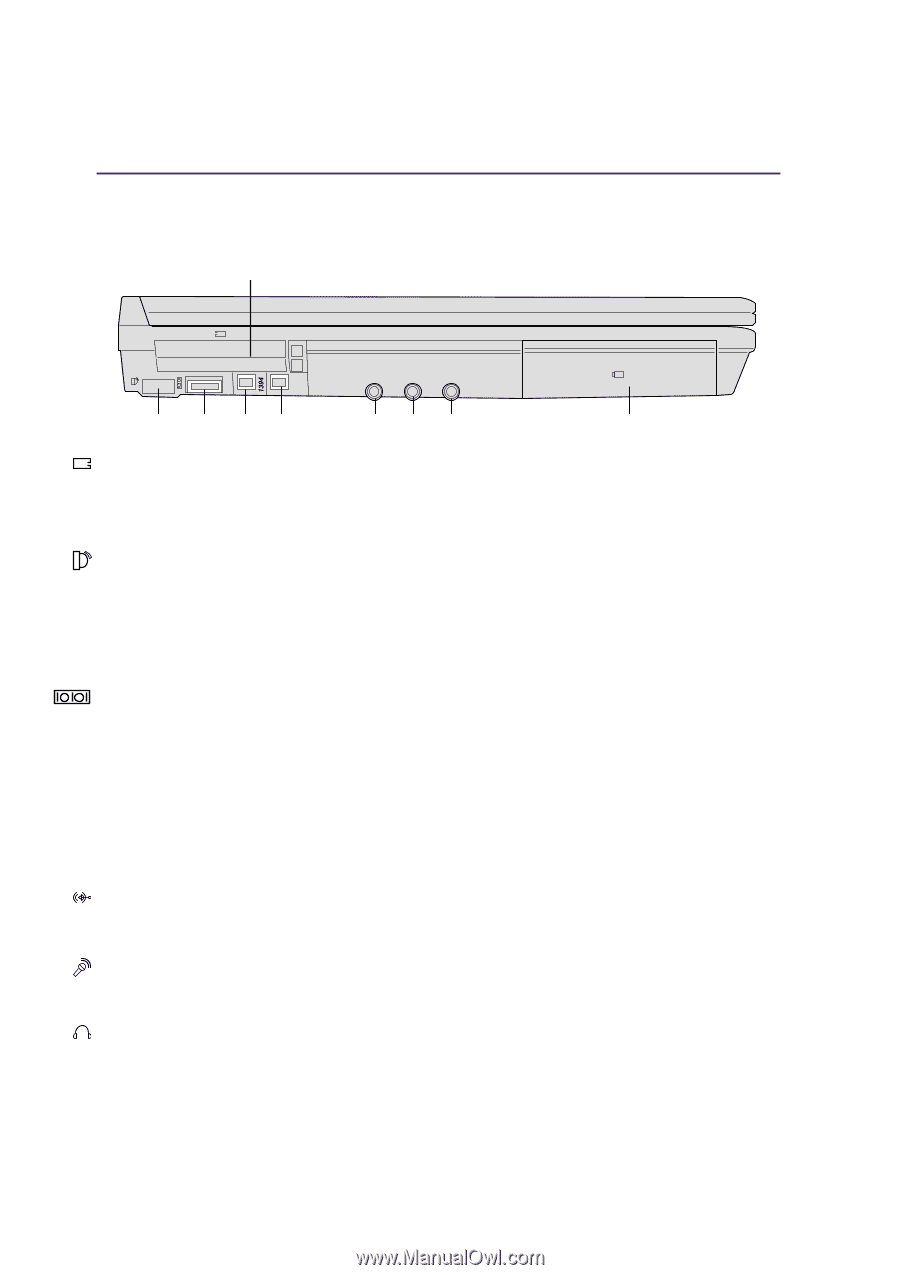
Left Side
 |
View all Asus L2E manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 18 highlights
2 Knowing the Parts Left Side Refer to the diagram below to identify the components on the left side of the Notebook PC. 2 PC Card (PCMCIA) Sockets Fast IrDA IO Port 2 IEEE 1394 Port Ports Audio In Mic-In Head-Out Battery Compartment (see bottom side) PC Card (PCMCIA) Socket and Eject Two PCMCIA 2.1 compliant sockets for two type I/II or one type III PC card is available. The sockets support 32-bit CardBus. This allows accommodation of Notebook PC expansion options such as memory cards, ISDN, SCSI, Smart Cards, and wireless network adapters. Fast Infrared Port (IrDA) The fast infrared (IrDA) communication port allows convenient wireless data communication with infrared-equipped devices or computers up to 4 Mbits/sec. This allows easy wireless synchronization with PDAs or mobile phones and even wireless printing to printers. If your office supports IrDA networking, you can have wireless connection to a network anywhere provided there is a direct line of sight to an IrDA node. Small offices can use IrDA technology to share a printer between several closely placed Notebook PCs and even send files to each other without a network. IO Port The IO port supports the 9-pin D-sub serial port adapter for serial devices such as a drawing tablet, serial mouse, PDA cradle, cellular phone link. 1394 IEEE1394 Port IEEE1394 is a high speed serial bus like SCSI but has simple connections and hot-plugging capabilities like USB. The interface IEEE1394 has a bandwidth of 100-400 Mbits/sec and can handle up to 63 units on the same bus. It is very likely that IEEE1394, together with USB, will replace Parallel, IDE, SCSI, and EIDE ports. IEEE1394 is also used in high-end digital equipment and should be marked "DV" for Digital Video port. Audio In Audio input allows feeding in audio from another source in order to listen to it using the Notebook PC's speakers or to use it for digital multimedia files. Microphone Jack (Mic-In) The mono microphone jack can be used to connect an external microphone or output signals from audio devices. Using this jack automatically disables the built-in microphone. Headphone Jack (Head-Out) The stereo headphone jack is used to connect the Notebook PC's audio out signal to amplified speakers or headphones. Using this jack automatically disables the built-in speakers. 18