Biostar TFORCE4 U TForce4 U user's manual - Page 15
RAID 0+1, Spanning JBOD - drivers download
 |
View all Biostar TFORCE4 U manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 15 highlights
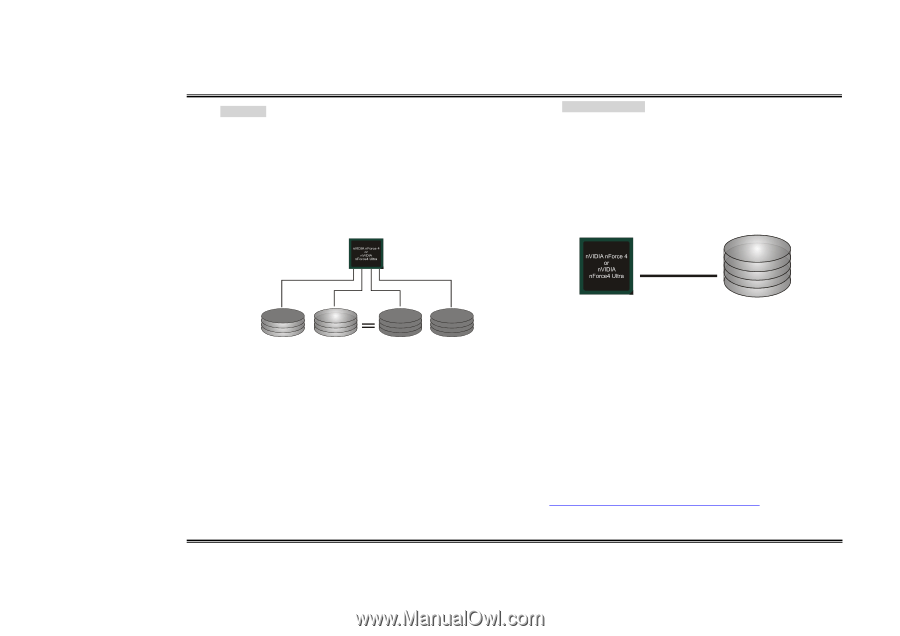
Biostar T-Series RAID 0+1: RAID 0 drives can be mirrored using RAID 1 techniques. Resulting in a RAID 0+1 solution for improved performance plus resiliency. Features and Benefits - Drives: Minimum 4, and maximum is 6 or 8, depending on the platform. - Benefits: Optimizes for both fault tolerance and performance, allowing for automatic redundancy. May be simultaneously used with other RAID levels in an array, and allows for spare disks. - Drawbacks: Requires twice the available disk space for data redundancy, the same as RAID level 1. - Fault Tolerance: Yes. Block 1 Block 3 Block 5 Block 2 Block 4 Block 6 Block 1 Block 3 Block 5 Block 2 Block 4 Block 6 TForce4/ TForce4 U Spanning (JBOD): JBOD stands for "Just a Bunch of Disks". Each drive is accessed as if it were on a standard SCSI host bus adapter. This is useful when a single drive configuration is needed, but it offers no speed improvement or fault tolerance. Features and Benefits - Uses: JBOD works best if you have odd sized drives and you want to combine them to make one big drive. - Benefits: JBOD provides the ability to combine odd size drives using all of the capacity of the drives. - Drawbacks: Decreases performance because of the difficulty in using drives concurrently. - Fault Tolerance: Yes. Single Logical Drive Disk 1: 40GB Disk 2: 80GB Disk 3: 40GB Disk 4: 120GB ※ For more detailed setup information, please refer to the Driver CD, or go to http://www.nvidia.com/page/pg_20011106217193.html to download NVIDIA nForce Tutorial Flash. 13 User's Manual