Casio FX250HC User Manual - Page 17
Coordinate Conversion, Permutation
 |
UPC - 079767108977
View all Casio FX250HC manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 17 highlights
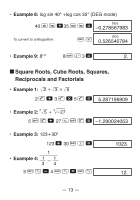
• Example 5: To convert 0.08125 grams to milligrams. .08125 J 81.25-03 • Example 6: To generate a random number between 0.000 and 0.999. Example (results differ each time) A c 0.664 kCoordinate Conversion • Example 1: To convert polar coordinates (r҃2, ҃60°) to rectangular coordinates (x, y). (DEG mode) x 2 A z 60 = DEG 1. y A N DEG 1.732050808 ANswaps displayed value with value in memory. • Example 2: To convert rectangular coordinates (1, 3 ) to polar coordinates (r, ). (RAD mode) r 1 A y 3 L = RAD 2. θ A N RAD 1.047197551 kPermutation • Example: To determine how many different 4-digit values can be produced using the numbers 1 through 7. 7 A m 4 = - 15 - 840.

— 15 —
81.25
–03
0.664
1.
DEG
2.
1.732050808
DEG
1.047197551
RAD
840.
Example (results differ each time)
RAD
•
Example 5:
To convert 0.08125 grams to milligrams.
.08125
J
•
Example 6:
To generate a random number between 0.000
and 0.999.
A
c
k
Coordinate Conversion
•
Example 1:
To convert polar coordinates (
r
µ
2,
²
µ
60°) to
rectangular coordinates (
x
,
y
). (DEG mode)
x
2
A
z
60
=
y
A
N
AN
swaps displayed value with value in memory.
•
Example 2:
To convert rectangular coordinates (1,
3 ) to
polar coordinates (
r
,
²
). (RAD mode)
r
1
A
y
3
L
=
θ
A
N
k
Permutation
•
Example:
To determine how many different 4-digit values
can be produced using the numbers 1 through 7.
7
A
m
4
=