Cisco 851W Configuration Guide - Page 121
Configuring Floating Static Routes, ip route, router rip, network
 |
UPC - 746320958071
View all Cisco 851W manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 121 highlights
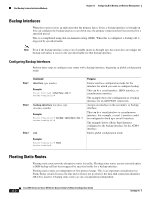
Chapter 13 Configuring Dial Backup and Remote Management Dial Backup Feature Activation Methods Note When static routes are configured, the primary interface protocol must go down in order to activate the floating static route. Configuring Floating Static Routes Static and dynamic routes are the two components of floating static routes. Perform these steps to configure the static and dynamic routes on your router, beginning in global configuration mode: Step 1 Command ip route prefix mask {ip-address | interface-type interface-number [ip-address]} Purpose Assigns the primary static route. Example: Router(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 22.0.0.2 Router(config)# Step 2 ip route prefix mask {ip-address | interface-type interface-number [ip-address]} [distance] Example: Router(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.2 150 Router(config)# Assigns the lower routing administrative distance value for the backup interface route. 192.168.2.2 is the peer IP address of the backup interface. Step 3 router rip Enables RIP routing. Example: Router(config)# router rip Router(config)# Step 4 network ip-address Example: Router(config)# network 22.0.0.0 Router(config)# Defines the primary interface network. 22.0.0.0 is the network value of the primary interface. Step 5 ip route prefix mask {ip-address | interface-type interface-number [ip-address]} [distance] Example: Router(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.2 150 Router(config)# Assigns the lower routing administrative distance value for the backup interface route. 192.168.2.2 is the peer IP address of the backup interface. OL-5332-01 Cisco 850 Series and Cisco 870 Series Access Routers Software Configuration Guide 13-3