Cisco NM-HD-1V= User Guide - Page 38
Global Storm-Control, Leaving a Multicast Group
 |
UPC - 746320823355
View all Cisco NM-HD-1V= manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 38 highlights
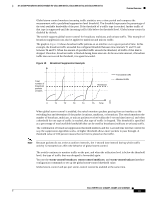
Feature Overview 16- and 36-Port Ethernet Switch Module for Cisco 2600 Series, Cisco 3600 Series, and Cisco 3700 Series Figure 17 Second Host Joining a Multicast Group Cisco router with Ethernet switch network module 1 CPU port Multicast Forwarding Table 88848 2 3 4 5 Host 1 Host 2 Host 3 Host 4 Table 8 Updated Multicast Forwarding Table Destination Address 0100.5e01.0203 Type of Packet !IGMP Ports 1, 2, 5 Leaving a Multicast Group The router sends periodic IP multicast general queries, and the switch responds to these queries with one join response per MAC multicast group. As long as at least one host in the VLAN needs multicast traffic, the switch responds to the router queries, and the router continues forwarding the multicast traffic to the VLAN. The switch only forwards IP multicast group traffic to those hosts listed in the forwarding table for that IP multicast group. When hosts need to leave a multicast group, they can either ignore the periodic general-query requests sent by the router, or they can send a leave message. When the switch receives a leave message from a host, it sends out a group-specific query to determine if any devices behind that interface are interested in traffic for the specific multicast group. If, after a number of queries, the router processor receives no reports from a VLAN, it removes the group for the VLAN from its multicast forwarding table. Global Storm-Control Global storm-control prevents switchports on a LAN from being disrupted by a broadcast, multicast, or unicast storm on one of the interfaces. A LAN storm occurs when packets flood the LAN, creating excessive traffic and degrading network performance. Errors in the protocol-stack implementation or in the network configuration can cause a storm. Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)XT, 12.2(8)T, and 12.2(15)ZJ 38