Compaq 307560-001 Novell GroupWise Performance Management on Compaq Servers - Page 13
Drive Spindles/Striping, Fault Tolerance
 |
UPC - 743172470379
View all Compaq 307560-001 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 13 highlights
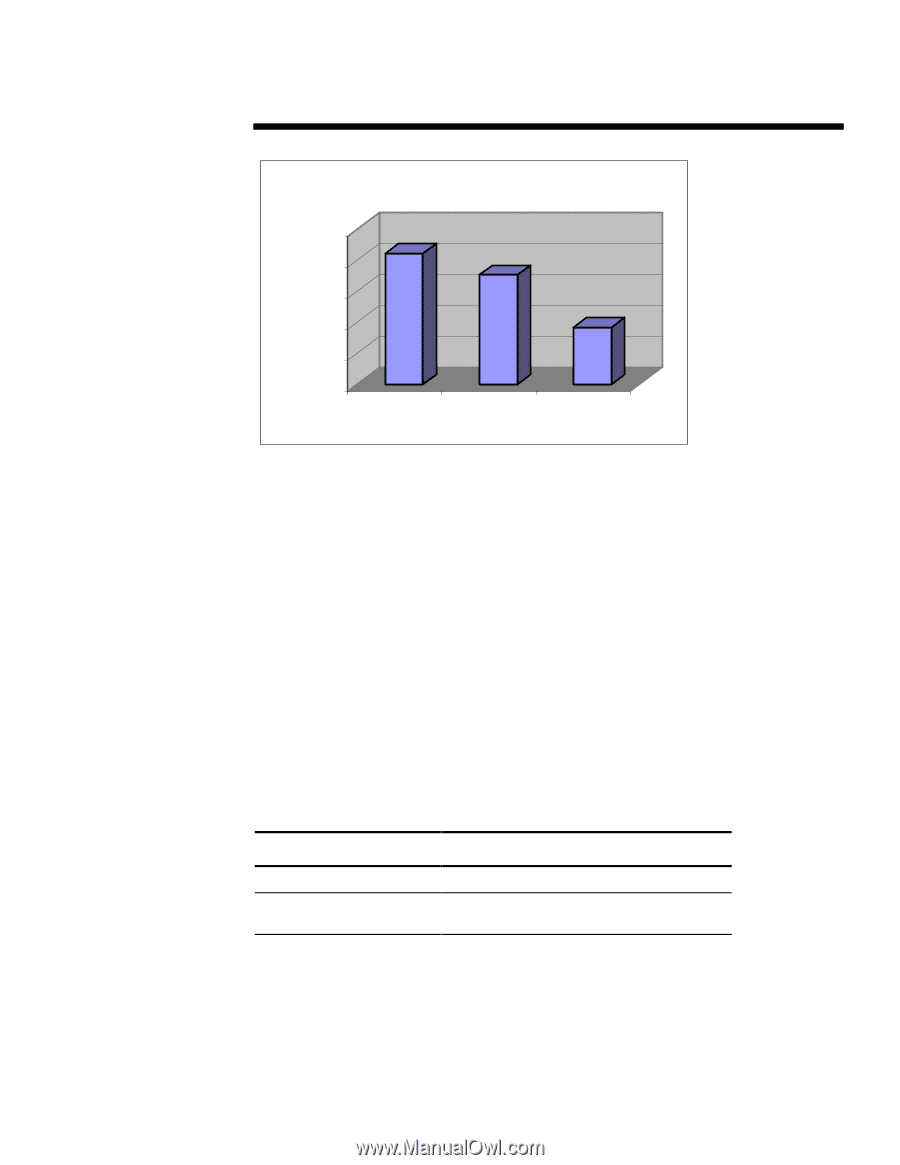
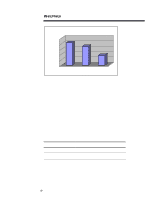
ECG007.0897 WHITE PAPER (cont.) 1...3 Performance Comparison of Volume Block Size Response Time (Seconds) 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 0 4KB 16KB 64KB Volume Block Size Figure 3. Volume Block Size Performance Comparison The test results show that there is a measurable difference in response time rates between various volume-block sizes. The large VBS will increase the performance by 100% from 64 KB over 16 KB. The large block size will also save a lot of memory to load the volume; therefore, we strongly recommend using the largest volume block size. Drive Spindles/Striping If your applications generate significant disk I/O, there will likely be a lot more concurrent use of system services. You can improve the performance of your disk subsystem under load conditions by having your hardware logical drive span multiple physical drives using "striping." Striping allows the data to be written "across" a series of physical drives that are viewed by the system as one logical drive. This data distribution across drives makes it possible to access data concurrently from multiple physical drives that have been defined as one logical drive array. Performance gains are achieved when you read from or write to the drive after the series of physical drives is united into one or more logical drive arrays. By distributing or striping the data evenly across the drives, it is then possible to access data concurrently from multiple drives in the series or array. The concurrent access of the data leads to higher I/O rates for the drive arrays than the spindles, thus improving your total system performance. Table 2. Drive Spindle Performance Comparison Mixed Load Response Time (Seconds) One Drive 823 8 Drives Hardware Striping (No 803 Fault Tolerance) Fault Tolerance The customer has several available options when configuring the GroupWise Server and making a decision about the level of fault tolerance the system requires. Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks (RAID)-level is a term used to refer to an array technology that provides data redundancy to increase the overall system reliability and performance. The fault tolerance method the customer selects effects the amount of available disk storage and the performance of the drive array.