D-Link DGS-1024D Product Manual - Page 12
Gigabit Ethernet Technology, 1P and QoS - gigabit dgs
 |
UPC - 790069268298
View all D-Link DGS-1024D manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 12 highlights
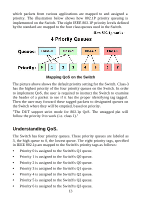
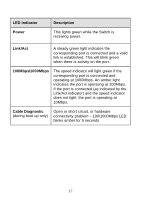
Gigabit Ethernet Technology Gigabit Ethernet is an extension of IEEE 802.3 Ethernet utilizing the same packet structure, format, and support for CSMA/CD protocol, full duplex, flow control, and management objects, but with a tenfold increase in theoretical throughput over 100-Mbps Fast Ethernet and a hundredfold increase over 10-Mbps Ethernet. Since it is compatible with all 10-Mbps and 100-Mbps Ethernet environments, Gigabit Ethernet provides a straightforward upgrade without wasting a company's existing investment in hardware, software and trained personnel. The increased speed and extra bandwidth offered by Gigabit Ethernet is essential to coping with the network bottlenecks that frequently develop as computers and their bus speeds get faster and more users use applications that generate more traffic. Upgrading key components, such as your backbone and servers to Gigabit Ethernet can greatly improve network response times as well as significantly speed up the traffic between your subnets. Gigabit Ethernet supports video conferencing, complex imaging and similar data-intensive applications. Likewise, since data transfers occur 10 times faster than Fast Ethernet, servers outfitted with Gigabit Ethernet NIC's are able to perform 10 times the number of operations in the same amount of time. 802.1P and QoS The DGS-1024D and DGS-1016D Switches support 802.1p priority queuing Quality of Service. The implementation of QoS (Quality of Service) and benefits of using 802.1p priority queuing are described here. Advantages of QoS QoS is an implementation of the IEEE 802.1p standard that allows network administrators a method of reserving bandwidth for important functions that require a large bandwidth or have a high priority, such as VoIP (voice-over Internet Protocol), web browsing applications, file server applications or video conferencing. Not only can a larger bandwidth be created, but other less critical traffic can be limited, so bandwidth can be saved. The Switch has separate hardware queues on every physical port to 12