D-Link DGS-1024D Product Manual - Page 16
Cable Diagnostic. - problems
 |
UPC - 790069268298
View all D-Link DGS-1024D manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 16 highlights
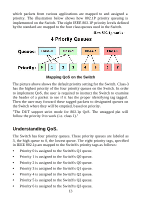
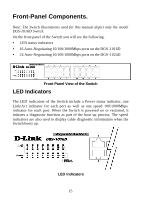
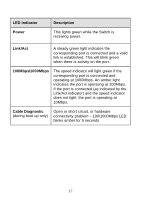
Cable Diagnostic. Upon booting up the Switch, a Cable Diagnostic is used to detect three problems that may prevent successful connection. This feature operates only on ports that are connected to 1000Mbps devices. If there are problems on a port connected to a Gigabit Ethernet device (1000Mbps), try restarting the Switch and watch the speed (100/1000Mbps) LED indicators to determine is the problem is a fault in the cable or connecting hardware. For ports operating at 10 or 100Mbps, the LED indicators can be used for less specific troubleshooting. The faults detected by the cable diagnostic for 1000Mbps operation are as follows: • Open circuit - a lack of continuity between the pins at each end of the Ethernet cable or a disconnected cable. • Short circuit - two or more conductors short-circuited. • Connectivity is checked for each of the eight wires of a cable to ensure its capability for running 1000Mbps. During the diagnostic, each port is scanned to determine if the Ethernet cable and connectors is in good working order. During the diagnostic process the speed LED for each port blinks green in sequential order. This port scan takes about 3 seconds. If a cable fault is detected, the corresponding port's speed LED will light amber for 5 seconds. The Switch is then reset for normal operation. It takes about 2 seconds for the Switch to reset. The entire Cable Diagnostic process takes about 10 seconds from the time the Switch is powered on. The table below summarizes Cable Diagnostic information. NOTE: the cable diagnostic function does not detect the length of Ethernet cabling. Remember that the length of cabling between two Ethernet devices may not exceed 100 meters (or 300 feet). 16