D-Link DGS-3308FG Product Manual - Page 228
Unidirectional Link, Packet Corruption, Resource Errors
 |
UPC - 790069239373
View all D-Link DGS-3308FG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 228 highlights
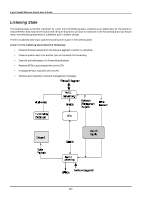
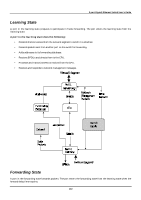
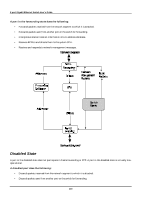
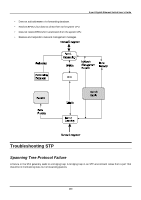
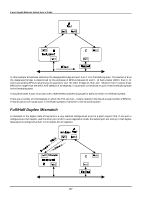
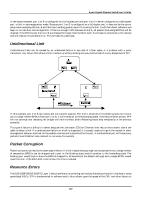
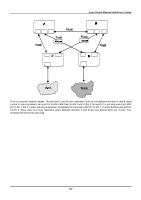
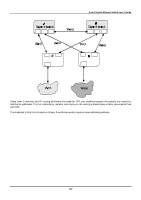
8-port Gigabit Ethernet Switch User's Guide In the above example, port 1 on B is configured as a full-duplex port and port 1 on A is either configured as a half-duplex port, or left in auto-negotiation mode. Because port 1 on B is configured as a full-duplex port, it does not do the carrier sense when accessing the link. B will then start sending packets even if A is using the link. A will then detect collisions and begin to run the flow control algorithm. If there is enough traffic between B and A, all packets (including BPDUs) will be dropped. If the BPDUs sent from A to B are dropped for longer than the MAX AGE, B will lose its connection to the root (A) and will unblock its connection to C. This will lead to a data loop. Unidirectional Link Unidirectional links can be caused by an undetected failure in one side of a fiber cable, or a problem with a ports transceiver. Any failure that allows a link to remain up while providing one-way communication is very dangerous for STP. In this example, port 2 on B can receive but not transmit packets. Port 2 on C should be in the blocking state, but since it can no longer receive BPDUs from port 2 on B, it will transition to the forwarding state. If the failure exists at boot, STP will not converge and rebooting the bridges will have no effect. (Note: Rebooting would help temporarily in the previous example). This type of failure is difficult to detect because the Link-state LEDs for Ethernet links rely on the transmit side of the cable to detect a link. If a unidirectional failure on a link is suspected, it is usually required to go to the console or other management software and look at the packets received and transmitted for the port. A unidirectional port will have many packets transmitted but none received, or vice versa, for example. Packet Corruption Packet corruption can lead to the same type of failure. If a link is experiencing a high rate of physical errors, a large number of consecutive BPDUs can be dropped and a port in the blocking state would transition to the forwarding state. The blocking port would have to have the BPDUs dropped for 50 seconds (at the default settings) and a single BPDU would reset the timer. If the MAX AGE is set too low, this time is reduced. Resource Errors The DGS-3308FG/DGS-3308TG Layer 3 switch performs its switching and routing functions primarily in hardware, using specialized ASICs. STP is implemented in software and is thus reliant upon the speed of the CPU and other factors to 218