Dell PowerConnect W-IAP108 Dell Instant 6.2.0.0-3.2.0.0 MIB Guide - Page 10
SNMP, High-Level MIB Hierarchy
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect W-IAP108 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 10 highlights
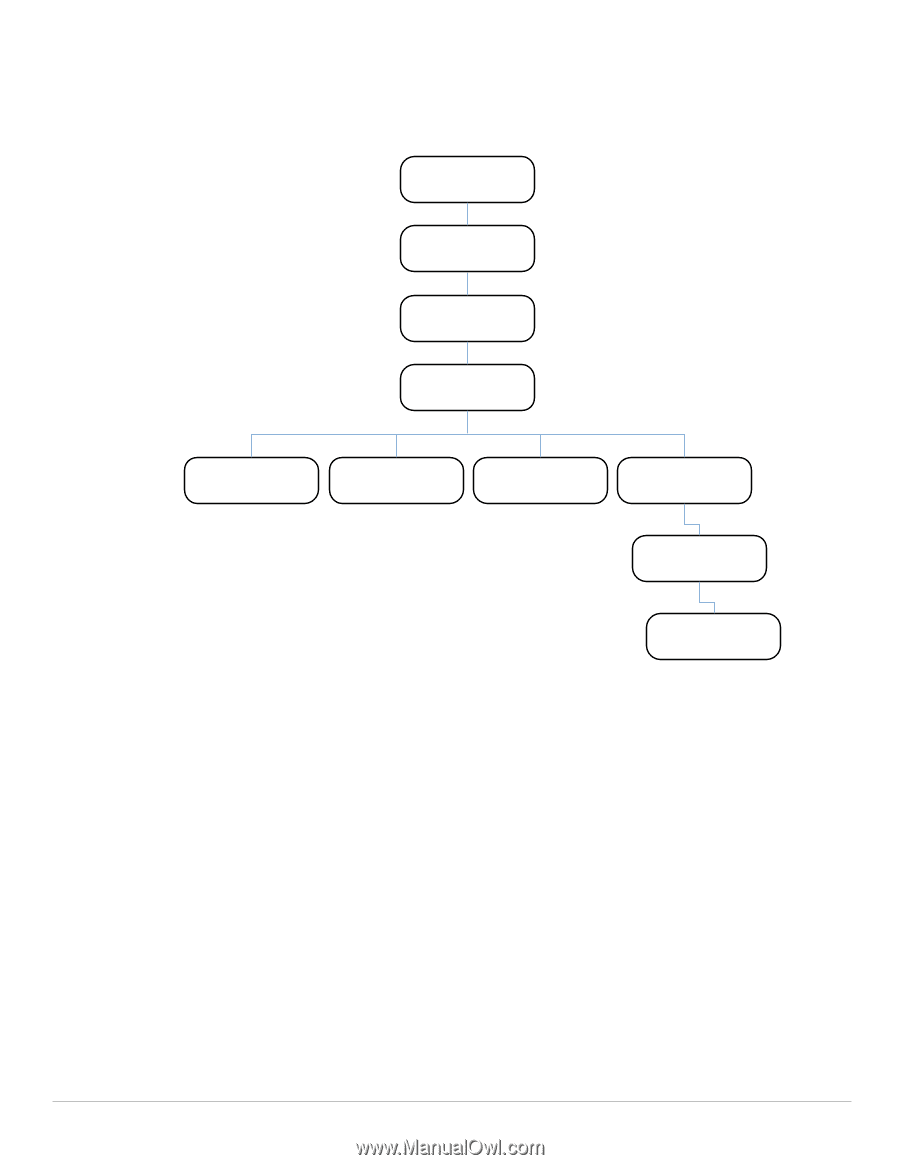
Figure 1 illustrates the high-level hierarchy of the MIBs. This document only covers the enterprise MIBs, objects designed to specifically support Dell devices. Standard MIBs are not covered. Figure 1 High-Level MIB Hierarchy ISO (1) ORG (3) DOD (6) Internet (1) 1 1.3 1.3.6 1.3.6.1 Directory (1) 1.3.6.1.1 Management (2) 1.3.6.1.2 Experimental (4) 1.3.6.1.3 Private (4) 1.3.6.1.4 Enterprises (1) 1.3.6.1.4.1 Aruba (14823) 1.3.6.1.4.1.14823 MIB is one of the elements of Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), which is used to manage network devices. To deliver information between devices, every object referred to in an SNMP message must be listed in the MIB. If a component of a device is not described in a MIB, that component cannot be recognized by SNMP- there is no information for SNMP managers and SNMP agents to exchange. The information provided by a MIB is a file that describes network elements with numerical strings. This information is compiled into readable text by the SNMP manager. For information about reading MIB text files, see "Reading MIB Files" on page 14. SNMP Three significant elements of SNMP are Managers, Agents, and MIBs. Managers (software application) are consoles that are used to communicate with and manage devices that support SNMP Agents. Managers collect information by polling Agents. Managers can also be used to send configuration updates or send controlling requests to actively manage a network device. Agents (software application) provide information from the network devices to the Managers. Network devices include workstations, routers, microwave radios, and other network components. 10 | MIBs Overview Dell PowerConnect W-Series Instant Access Point | MIB Reference Guide