Dell PowerConnect W-IAP92 Dell Instant 6.1.2.3-2.0.0.0 MIB Reference Guide - Page 21
Snmp
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect W-IAP92 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 21 highlights
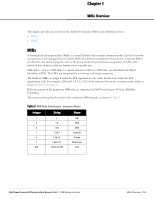
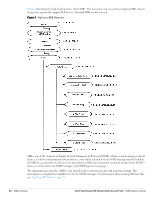
SNMP Three significant elements of SNMP are Managers, Agents, and MIBs. Managers (software application) are consoles that are used to communicate with and manage devices that support SNMP Agents. Managers collect information by polling Agents. Managers can also be used to send configuration updates or send controlling requests to actively manage a network device. Agents (software application) provide information from the network devices to the Managers. Network devices include workstations, routers, microwave radios, and other network components. Agents are embedded in the Dell PowerConnect W-Series Mobility Controllers firmware, unlike some devices such as servers that require the agent to be installed separately. MIBs are used for communication between the Managers and the Agents. The OIDs of the MIBs enable the Managers and Agents to communicate specific data requests and data returns. To ensure functionality with SNMP, MIB objects must be defined with the proper keywords, as shown in Table 4. ArubaOS Enterprise MIBs support SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3. Table 4 MIB Keywords Keyword Description Sequence Syntax Max-Access Status Description The sequence of objects of the MIB. This keyword is used mostly with entry MIB objects to list the MIB objects that exchange information. Textual conventions, such as Integer32. Defines the object accessibility: read-only: can be retrieved but not modified read-write: can be retrieved and modified not-accessible: cannot be retrieved; it is for internal (device) use only accessible-for-notify: can be retrieved when a trap message (notification) is sent Defines the status of the object: current: up to date and valid. deprecated.: indicates an obsolete definition. It permits new or continued implementation to maintain interoperability with existing implementations. obsolete: obsolete. It should not be implemented and/or can be removed if previously implemented. A text string that describes the object. Dell PowerConnect W-Series Instant Access Point | MIB Reference Guide MIBs Overview | 21