Dell VNX5800 VNX Series: Introduction to SMB 3.0 Support - Page 18
BranchCache V2, SMB Encryption
 |
View all Dell VNX5800 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 18 highlights
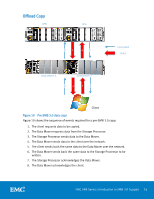
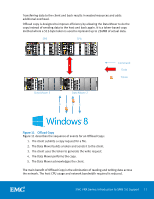
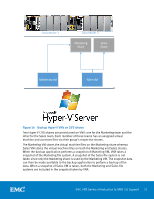
Offload copy is only used for files that are greater than 512 KB as the token overhead would make it impractical for smaller files. Note that if the data that is represented by the token is modified, the token is invalidated and an error is returned. The client then reverts back to the old copy method using a standard read and write. BranchCache V2 BranchCache is a Microsoft feature that was originally introduced in the Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 operating systems. It is designed to optimize wide area network (WAN) bandwidth when one or more remote branch offices need to connect to the main office to retrieve data. This had several disadvantages including poor application responsiveness, high WAN link utilization, and WAN bandwidth is expensive. When BranchCache is enabled, it creates a cache of the content from the DM, locally within a branch office. A client from the same network can request the file and download it from the local cache, instead of downloading it from the wide area network. BranchCache optimizes the local link utilization and the responsiveness of applications, and reduces the WAN bandwidth consumption. When a file is requested from the DM in the main office, a hash of the file is sent to the client instead of the file itself. The hash, known as the signature, is much smaller than the file itself and the client uses it to search the branch office for the file. If a match is found at the branch office, the client will retrieve the file using the LAN. If no match is found, the client retrieves the file through the WAN and caches it for other clients at the branch. An update to BranchCache was released in Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 called BranchCache V2. In the original BranchCache, files were divided into 32 MB segments and each segment was divided into 65KB blocks. Each block was hashed using SHA256 to generate the signature. In BranchCache V2, a simpler format was introduced to increase the likelihood of finding signature matches. The concept of blocks has been dropped. Files are divided into segments and each segment is hashed using SHA256 to generate the signature. VNX uses a fixed segment size of 128KB. SMB Encryption SMB encryption provides secure access to data over untrusted networks by providing end-to-end encryption between the client and VNX. It does not require specialized hardware, IPSec, or WAN accelerators. Scenarios where SMB encryption can be utilized include Remote Office Branch Office (ROBO) over WAN networks and application workloads over unsecured networks. Encryption at the share-level is enabled on the particular share, and encryption is enforced when that share is accessed. Optionally, encryption can be enforced at the EMC VNX Series: Introduction to SMB 3.0 Support 18