Epson 1250 Technical Brief (Scanners) - Page 5
Color CCD - perfection
 |
UPC - 010343836976
View all Epson 1250 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 5 highlights
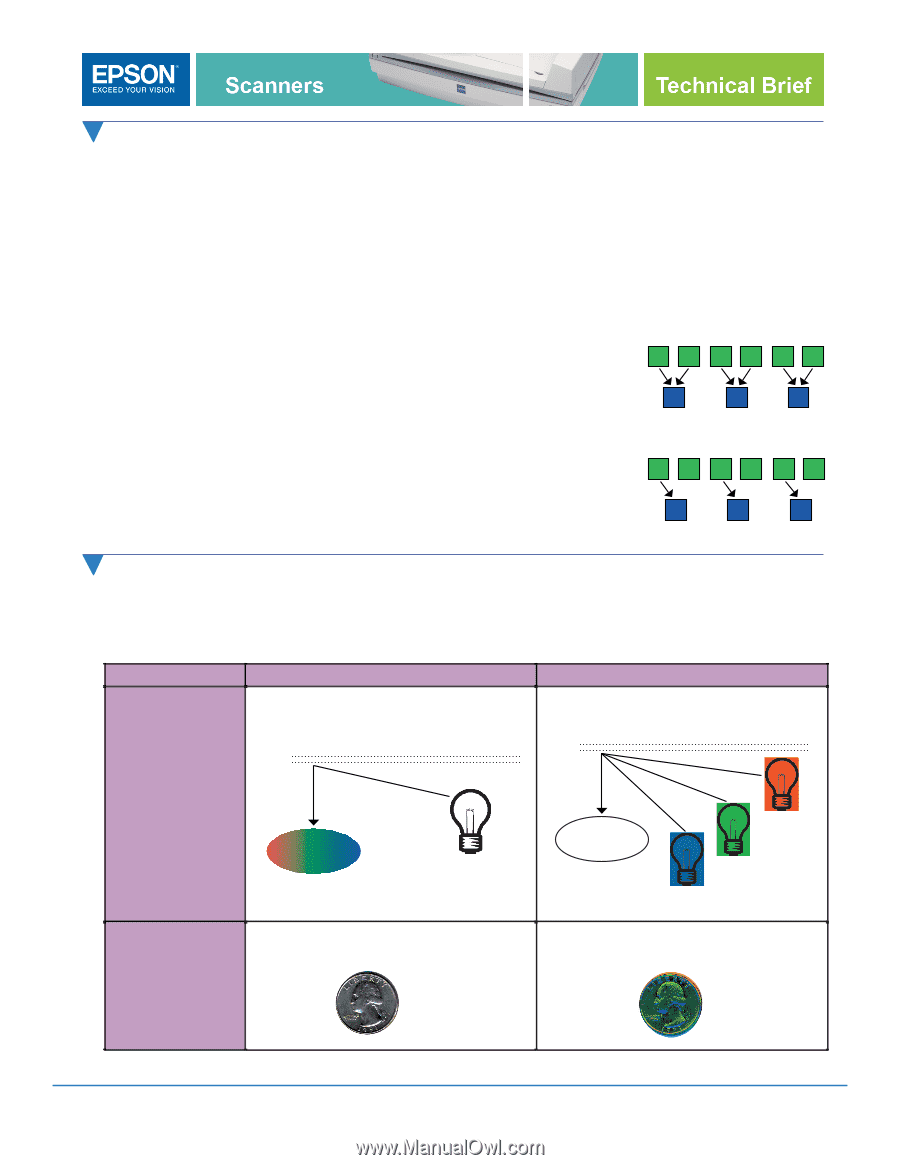
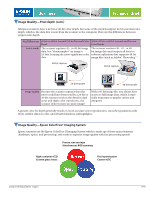
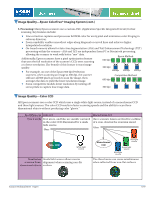
Image Quality-Epson ColorTrue® Imaging System (cont.) 3. Processing: Many Epson scanners use a custom ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit) for fast scanning. Key features include: Line correction captures and processes full RGB color for every pixel and minimizes color fringing in subscan direction. Zoom capability enables smoothest edges along diagonal or curved lines and achieves higher interpolated resolution On-board memory allows for Auto Area Segmentation (AAS) and Text Enhancement Technology (TET) processing within the scanner-AAS and TET are independent from PC or Macintosh processing, allowing the scanner to work with better "raw" data. Additionally, Epson scanners have a pixel optimization feature that uses the full resolution of the scanner's CCD, even scanning 600 dpi Epson Method: at a lesser resolution. The benefit of this feature is truer image quality. 300 dpi For example, on one of the Epson 600 dpi Perfection Average Average Average scanners, when scanning an image at 300 dpi, the scanner still uses all 600 pixels per inch to scan the image, then averages the data to yield the lower resolution image. Competitive Method: 600 dpi On Off On Off On Off Some competitive models lower resolution by turning off some pixels to capture less image data. 300 dpi Image Quality-Color CCD All Epson scanners use a color CCD which uses a single white light source, instead of a monochrome CCD and three light sources. The color CCD results in faster scanning speeds and the ability to scan threedimensional objects without producing color "ghosts." Key Differences Color CCD How it works Red, green, and blue are quickly captured in the color CCD illuminated by a single light source. Glass Monochrome CCD three separate lamps are fired for eachline of a scan, slowing the scanning speed. Glass Color CCD White light source Result when Single light source allows precise scanning three- alignment when scanning non-flat dimensional objects surfaces Monochrome CCD Red light source Green light source Blue light source The three lamps can cause misalignment when reflected from non-flat surfaces. Scanner Technical Brief-Page 5 6/07