Fluke 175 FE 175,177,179 Users Manual - Page 13
Measuring Frequency, Using the Bar Graph
 |
View all Fluke 175 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 13 highlights
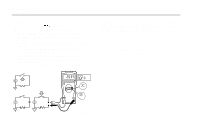
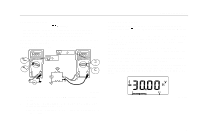
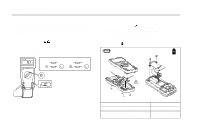
XW Measuring Frequency Warning To avoid electrical shock, disregard the bar graph for frequencies > 1 kHz. If the frequency of the measured signal is > 1 kHz, the bar graph is unspecified. The Meter measures the frequency of a signal. The trigger level is 0 V, 0 A AC for all ranges. AC/DC Voltage Frequency AC Current Frequency x 2 Hz V HOLD MIN MAX RANGE Hz HOLD MIN MAX RANGE mA V A + + Using the Bar Graph Using the Bar Graph The bar graph is like the needle on an analog Meter. It has an overload indicator ( ) to the right and a polarity indicator (±) to the left. Because the bar graph updates about 40 times per second, which is 10 times faster than the digital display, the bar graph is useful for making peak and null adjustments and for observing rapidly changing inputs. The bar graph is disabled when measuring capacitance or temperature. In frequency, the bar graph accurately indicates the voltage or current up to 1 kHz. The number of lit segments indicates the measured value and is relative to the full-scale value of the selected range. In the 60 V range, for example (see below), the major divisions on the scale represent 0, 15, 30, 45, and 60 V. An input of −30 V lights the negative sign and the segments up to the middle of the scale. AIK09F.EPS ⇒ To exit frequency, press YELLOW button or turn the rotary switch. ⇒ In frequency, the bar graph shows the AC/DC voltage or AC current accurately up to 1 kHz. ⇒ Select progressively lower ranges using manual ranging for a stable reading. AIK11F.EPS 9