HP 6s HP 6S Scientific Calculator - (English) User's Guide - Page 17
Logical operations, Binary, octal and hexadecimal values
 |
View all HP 6s manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 17 highlights
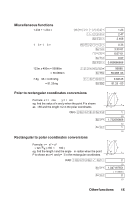
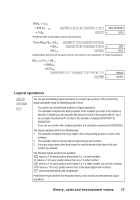
76548 ÷ 1210 = 334.33….10 M§7654dM¤12= 334.3333333 = 5168 M§ OCT 516. Fractional parts of calculation results are truncated. 1102+4568x7810÷1A16 M¥110+M§456* =39016 M¤78dM¦1A= HEX 390. =91210 M¤ 912. Multiplication and division are given priority over addition and subtraction in mixed calculations. BC16 x (1410 + 6910 =1560410 =3CF416 M¦BC*(M¤14+69)= M¦ HEX 15604. 3CF4. Logical operations &o xX Ì You can use the following logical operations to compare two numbers. When performing logical operations, keep the following points in mind: • You cannot use decimal-base numbers in logical operations. • The calculator compares the binary versions of the numbers you enter. If the number is less than 10 digits long, the calculator fills values to the left of the number with 0s—eg, if you compare hexadecimal F1 to octal 4, the calculator compares 0000010001 to 0000000100. • If you use one number with a logical operation, the calculator compares it to 0000000000. The logical operators work in the following way: 1. The operation compares the binary digits in the corresponding positions in each of the numbers. 2. The operation returns a binary digit corresponding to each position. 3. If you are using a base other than binary, the result is shown in the base of the last number you entered. The following logical operators are available: & returns a 1 for every position where there is a 1 in both numbers. o returns a 1 for every position where there is a 1 in either number. x returns a 1 for every position where there is a 1 in either number, but not both numbers. X returns a 1 for every position where there is the same digit in both numbers. Ì returns the diminished radix complement. Press these keys to perform the respective binary, octal, decimal and hexadecimal logical operations. Binary, octal and hexadecimal values 17