HP F2222A#ABA hp 9g_user's manual_manuel de l'utilisateur_EF_HDP1SG181S5.pdf - Page 98
HP F2222A#ABA - 9s Scientific Calculator Manual
 |
UPC - 808736452823
View all HP F2222A#ABA manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 98 highlights
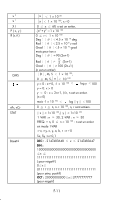
x 2 x -1 X ! P ( x, y ) R (r,θ) DMS nPr, nCr STAT BaseN x < 1 × 10 50 x < 1 × 10 100, x≠0 0 ≦ x ≦ 69, x est un entier. x2 + y2 <1 x 10 100 0 ≦ r< 1 × 10 100 Deg 4.5 × 10 10 deg Rad 2.5 × 10 8πrad Grad 5 × 10 10 grad mais pour tan x Deg 90 (2n+1) π Rad 2 (2n+1) Grad 100 (2n+1) (n est un entier) │D│, M, S < 1 × 10 100, 0 ≦ M, S, x < 10 100 y > 0 : x≠0, -1 × 10 100 < log y <100 y = 0: x > 0 y < 0 : x = 2n+1, I/n, n est un entier. (n≠0) mais -1 × 10 100 < log | y | <100 0 ≦ r ≦ n, n < 10 100, n, r sont entiers. | x | < 1×10 100,| y | < 1×10 100 1 -VAR : n ≦ 30, 2 -VAR : n ≦ 30 FREQ. = n, 0 ≦ n < 10 100 : n est un entier en mode 1-VAR σx,σy, x, y, a, b, r : n≠0 Sx, Sy :n≠0,1 DEC : - 2147483648 ≦ x ≦ 2147483647 BIN : 10000000000000000000000000000000 ≦x ≦ 11111111111111111111111111111111 ( pour négatif ) 0≦x≦ 01111111111111111111111111111111 (pour zéro, positif) OCT : 20000000000≦x≦37777777777 (pour négatif) F-11