HP Integrity NonStop NB50000c HP BladeSystem c-Class architecture - Page 5
Scalable blade form factors
 |
View all HP Integrity NonStop NB50000c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 5 highlights
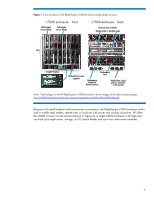
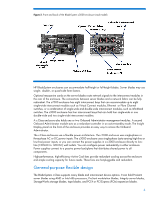
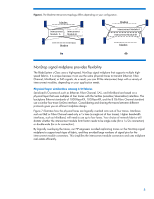
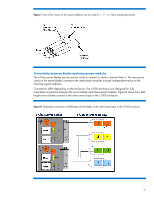
BladeSystem interconnect modules support a variety of networking standards including Ethernet, Fibre Channel, FCoE, InfiniBand, iSCSI, and Serial Attached SCSI (SAS). The BladeSystem c-Class architecture is a basis for broad solutions including the HP BladeSystem Matrix (www.hp.com/go/matrix). Matrix provides shared IT infrastructure services by using pools of compute, storage, and networking capabilities, integrated with management tools to provision, optimize, and protect the infrastructure. The BladeSystem c-Class interoperates and connects with other HP infrastructure pieces, including external storage components such as DAS (direct-attached storage), NAS (network attached storage), and SAN (storage area network) solutions (www.hp.com/go/blades/storage). The design supports flexibility: Blade form factors that can scale vertically or horizontally-half-height or full-height blades and single-, double-, or quad-wide blades Interconnect module form factors that can scale-single-wide or double-wide modules Signal midplane that allows flexible use of I/O signals, supporting multiple fabrics using the same traces. Scalable blade form factors HP engineers chose the half-height and full-height blade form factors (scaling blades vertically in the c7000 enclosure and horizontally in the c3000 enclosure) to support cost, reliability, and ease-of-use requirements. Being able to use either full or half-height form factors in the same enclosure lets you make more efficient use of space (Figure 3). For example, you can fill the enclosure with highperformance full-height server blades, or you can use a mixture of the two form factors. The size of the full-height blades allows enough room to include two signal connectors on the same printed circuit board (PCB) plane for reliable and simple connectivity to the NonStop signal midplane. The BladeSystem enclosures use a removable, tool-less divider to hold the half-height blades in the enclosure. See "Technologies in the HP BladeSystem c7000 Enclosure" or "HP BladeSystem c3000 Enclosure" at http://h18004.www1.hp.com/products/servers/technology/whitepapers/proliantservers.html#bl for configurations. The device bay thickness offers several advantages over either narrower or wider alternatives: Holds industry-standard components Holds enough blades to amortize the cost of the shared enclosure infrastructure (power supplies and fans). Uses cost effective, standard-height DIMMs in the server blades. Uses vertical (rather than angled) DIMM connectors to give better signal integrity, more room for heat sinks, allow more DIMM slots per processor, and provide better airflow across the DIMMs. 5