HP LH4r Architecture/Technology Overview - Page 6
Enhanced Software, Improving System Uptime: Availability, Redundancy, Automated Failure Recovery
 |
View all HP LH4r manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 6 highlights
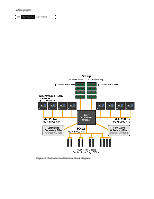
ZKLWHýSDSHU +3ý 1HW6HUYHUý /;Uýåèíí Enhanced Software Intel has released new instructions associated with the Pentium III Xeon processors. These instructions are called Streaming Single Instruction, Multiple Data (SIMD) Extensions. These extensions serve to boost the performance of TCP/IP-based applications for messaging, Internet- and intranet-related functions. Other business-critical applications such as database and ERP applications will also benefit, achieving notable performance increases. SIMD extensions help memory-intensive applications use the system resources more efficiently when processing computing tasks. System efficiencies increase because the extensions give these applications their instructions on using main memory, L1 and L2 caches to accelerate application performance. SIMD extensions also streamline the TCP/IP stack, which improves the functionality of streaming media applications such as voice recognition or compression software, as well as Web hosting and e-commerce transactions. Improving System Uptime: Availability Beyond building reliable, high quality servers, HP has implemented a number of techniques to improve server uptime, a critical measure for data centers, where the data must always be accessible to the users. Redundancy HP has provided redundancy (a means of preventing failures) for several components and subsystems in the design of the HP NetServer LXr 8500. For example, power supplies and fans are included at the N+1 level, one more than is required to support the system. Should one fail, the others can assume the load until the failed one is replaced. Additionally, since both the fans and power supplies are hot swappable, the server can continue to run while the repairs are made. HP has also designed for processor redundancy, de-allocating a processor should it fail. The system will also de-allocate failed memory DIMMs, a failed processor bus or a failed memory board. The system will still boot up, loading the NOS while ignoring the failed component. (This capability assumes a configuration that contains at minimum, two buses, two memory boards and two DIMMs.) Automated Failure Recovery Should a system fail, automated failure recovery allows for quick recovery from a failure. Features in this category include automatic server restart (ASR), Error Checking and Correcting (ECC) memory and new data backup capabilities. HP is the first major server vendor to offer a hardware-based One-Button DisasterRecovery tape backup solution. Without needing technical assistance, customers simply can insert the most recent backup tape and push one button on their HP SureStore DDS tape drive. The system will automatically boot from the tape drive, restoring the operating system, configurations, applications, device drivers and files to exactly the way they were at the time of the last backup. 6