HP Rp5405 BSD Sockets Interface Programmer's Guide - Page 121
The O_NDELAY flag
 |
View all HP Rp5405 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 121 highlights
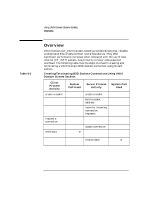
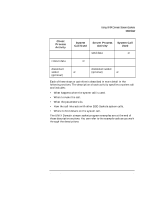
Advanced Topics for Internet Datagram Sockets Nonblocking I/O Nonblocking I/O Sockets are created in blocking mode I/O by default. You can specify that a socket be put in nonblocking mode by using the ioctl system call with the FIOSNBIO request. An example usage of this call is: #include ... ioctl(s,FIOSNBIO,&arg); arg is a pointer to int: • When int equals 0, the socket is changed to blocking mode. • When int equals 1, the socket is changed to nonblocking mode. If a socket is in nonblocking mode, the following calls are affected: recvfrom If no messages are available to be received, recvfrom returns the value -1 and the EWOULDBLOCK error. This is also true for recv and read. sendto If there is no available message space for the message to be transmitted, sendto returns the value -1 and the EWOULDBLOCK error. The O_NDELAY flag for fcntl(2) is also supported. If you use this flag and there is no message available to be received on a recv, recvfrom, or read call, the call returns immediately with the value of 0. If you use the O_NONBLOCK flag, the call returns immediately with the value of -1 and the EAGAIN error. This is the same as returning an end-of-file condition. This is also true for send , sendto, and write if there is not enough buffer space to complete the send. The O_NDELAY and O_NONBLOCK flags have precedence over the FIOSNBIO flag. Setting both the O_DELAY and O_NONBLOCK flags is not allowed. Chapter 5 121