HP Rp5405 BSD Sockets Interface Programmer's Guide - Page 91
When to Get Server's Socket Address
 |
View all HP Rp5405 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 91 highlights
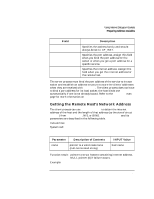
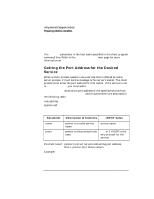
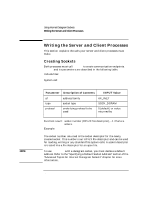
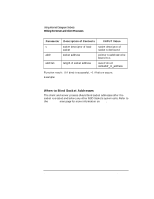
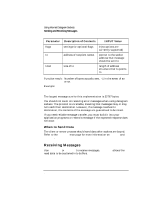
Using Internet Datagram Sockets Preparing Address Variables When to Get Server's Socket Address The server process should get the server's socket address before binding. The client process should get the server's socket address before client requests the service from the host. Refer to the getservent(3N) man page for more information on getservbyname. Using a Wildcard Local Address Wildcard addressing simplifies local address binding. When an address is assigned the value of INADDR_ANY, the host interprets the address as any valid address. This means that the server process can receive on a wildcard address and does not have to look up its own internet address. For example, to bind a specific port address to a socket, but leave the local internet address unspecified, the following source code could be used: #include #include #include ... struct sockaddr_in sin; ... s = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0); sin.sin_family = AF_INET; sin.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY; sin.sin_port = MYPORT; bind (s, &sin, sizeof(sin)); Chapter 4 91