HP StorageWorks Modular Smart Array 1000 HP StorageWorks MSA1000 Configuration - Page 4
MSA1000 Installation and Configuration Best Practices, MSA1000 Features
 |
View all HP StorageWorks Modular Smart Array 1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 4 highlights
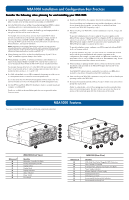
MSA1000 Installation and Configuration Best Practices Consider the following when planning for and installing your MSA1000: ● Complete the Planning Worksheet on the opposite side of this document to help you gather all of the items required for installing your MSA1000. ● Go to the MSA1000 website at http://www.hp.com/go/msa1000 to confirm your plans and review current information about your MSA1000. ● When planning your LUNs, customize the RAID type and striping method to the type of data that will be stored on the array. For example, for non-critical data, you may want to use RAID 0, which provides no fault tolerance, but provides rapid storage of large amounts of data. For critical data, use RAID 1 (RAID 1+0), RAID 5, or RAID ADG, choosing the RAID type the offers the desired combination of fault-tolerance, I/O performance, and capacity utilization. Note: Depending on the number of drives that you include in an array, the ACU automatically assumes a default RAID type of ADG, which maximizes fault tolerance and capacity utilization, but at a significant cost of I/O performance. For comparable fault tolerance but higher performance, consider using RAID 1+0. ● When planning your LUNs, set the drive rebuild priority of your LUNs to "high" to minimize exposure during a drive failure. ● When planning your LUNs, to optimize performance and redundancy in a mirrored environment (RAID 1 or RAID 1+0), stripe the drives in the array across the separate buses within the MSA1000 and any attached enclosures. For example, because drive bays 1-7 in the MSA1000 are located on bus 1 and bays 8-14 are located on bus 2, when creating a mirrored array with 6 drives, include the drives in bays 1, 2, 3, and 8, 9, 10. ● In a SAN with multiple-servers, HP recommends designating one of the servers as a management server, to centralize your management tasks. It is on this server that you will install management software such as the ACU, and it is from this server that you will perform your SAN management tasks. ● Use the HP StorageWorks MSA1000 Installation Guide to actually install and configure your MSA1000. Details are available in the installation guide that are not provided in this Overview poster. ● Install your MSA1000 in the sequence listed in the installation guide. Several installation and configuration steps include dependencies and if you deviate from the listed sequence, you may have to un-install and then re-install your MSA1000, beginning at step 1. ● Before installing your MSA1000, consider redundancies of power, storage, and data paths. To provide redundant power, be sure to plug the two power supplies on the MSA1000 into separate Uninterruptable Power Supplies (UPS) on separate power sources. If you only have 1 UPS, maintain separate power paths by plugging one MSA1000 power supply to the UPS on one power source and plug the other MSA1000 power supply to a separate power source. To provide redundant storage, configure your LUNs using fault-tolerant RAID levels and striping methods. To provide redundant data paths, you must include two isolated fibre channel fabrics and the associated hardware and software components in the configuration. (For example, you must include two MSA1000 controllers, two interconnect devices, and two HBAs in each server. Environments using Secure Path software must install the software on each server.) ● When installing or updating the HBA drivers, always use the drivers and the installation scripts provided on the MSA1000 Support Software CD or the MSA1000 website. Your MSA1000 will not operate as intended if you update your HBA driver manually or use drivers obtained from the HBA manufacturer. ● After installing your MSA1000, remember to set your host mode to identify your operating system to the MSA1000. ● If you need to install Secure Path software, be sure to follow every server reboot prompt that is presented. Failure to acknowledge a server reboot prompt may result in your path redundancy not functioning properly. Be sure to reboot your server after the server portion of the install and again after the client portion of the install. MSA1000 Features Two views of the MSA1000 are shown, with the key components identified. 2 1 8 Reference # 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 MSA1000 (Front View) Identifier Redundant Controller Slot Blank Primary MSA1000 Controller Display Buttons Display Panel Display Indicators Status Indicators Power Switch Drive Bay(s) 3 3 2 4 1 5 6 4 7 5 9 8 76 Reference # 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 MSA1000 (Rear View) Identifier 2-Gb Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP) Transceiver Fibre Channel I/O Module Redundant Fibre Channel I/O Module Slot (Blank) Power Supply Indicators Blowers Attached to Power Supply SCSI Expansion Port A SCSI Expansion Port B Environmental Monitoring Unit Indicators Environmental Monitoring Unit