HP StorageWorks XP12000 HP StorageWorks XP Disk Array Configuration Guide: Non - Page 14
Connecting the disk array, Defining the paths
 |
View all HP StorageWorks XP12000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 14 highlights
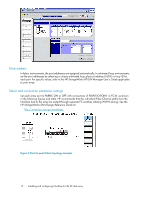
• Do not connect other operating systems to the same XP ports or even use a port that shares a processor with the same port as NonStop systems. • Use SAN switches dedicated to NonStop connections, or solutions that have been qualified by HP. These HP-qualified solutions can include operating systems other than NonStop, but fabric zoning and LUN security must be used to isolate them from the NonStop systems. Table 3 Fabric zoning and LUN security settings Environment Single node SAN Multiple node SAN Fabric Zoning Not required Not required LUN Security Must be used Must be used Connecting the disk array The HP service representative connects the disk array to the host by: 1. Verifying operational status of the disk array channel adapters, LDEVs, and paths. 2. Connecting the Fibre Channel cables between the disk array and the fabric switch or host. 3. Verifying the ready status of the disk array and peripherals. Defining the paths Use XP Remote Web Console (shown), XP Command View, or XP Command View Advanced Edition to define paths (LUNs) between hosts and volumes in the disk array. For non-host mirrored disks, create two identical host groups on two different ports (one port in each cluster in the array) with identical LUNs in each group. For host mirrored disks, create two sets of two identical host groups (four total host groups). Configure one set of two host groups for the Primary (P) path and its backup (B). Assign these two host groups to two different ports in two different clusters of the disk array, and give each host group access to separate but identical LUNs. Configure the other set of two host groups for the Mirror (M) and Mirror Backup (MB) paths. Assign these two host groups to two different ports in two different clusters of the disk array, and give each host group access to separate but identical LUNs. This arrangement minimizes the shared components among the four paths, providing both mirroring and greater failure protection. NOTE: For the highest level of availability and fault tolerance, HP recommends the use of two XP disk arrays, one for the Primary disks and one for the Mirror disks. This process is also called "LUN mapping." In XP Remote Web Console and XP Command View, LUN mapping includes: • Configuring ports • Enabling LUN security on the ports • Creating host groups • Assigning Fibre Channel ServerNet adapter WWNs to host groups • Mapping volumes (LDEVs) to host groups (by assigning LUNs) 14 Installing and configuring NonStop for the XP disk array