HP dx6050 Configuring Graphics Memory for HP Business PC dx6050 - Page 8
Example 3, integrated graphics is still hidden from the operating system and cannot be used
 |
View all HP dx6050 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 8 highlights
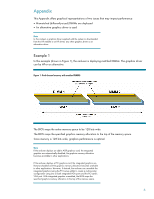
Example 3 In this example (shown in Figure 3), the end-user is deploying mismatched DIMMs. There is an alternative graphics driver. Note An alternative graphics driver may behave differently than an HP driver if memory is mismatched, as in this example. Figure 3: Dual-channel memory with mismatched DIMMS, alternative graphics driver. The BIOS maps upper memory to be 64 bits wide, lower memory to be 128 bits wide. The BIOS maps the specified graphics memory allocation to the top of the memory space (part of the larger DIMM). The allocation is 64 bits wide. An alternative driver may automatically re-map the graphics allocation to the faster 128-bit memory space to optimize graphics performance. However, the space originally allocated by the BIOS for integrated graphics is still hidden from the operating system and cannot be used, reducing the amount of memory available for other applications. In addition, boot time may increase substantially as data from upper memory are copied to the 128bit space. 8