Intel DH57DD Intel Desktop Board DH57DD Product Guide English - Page 47
S/PDIF Header, Serial Header, Consumer IR (CIR) Headers, Table 10. S/PDIF Header Signal Names
 |
View all Intel DH57DD manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 47 highlights
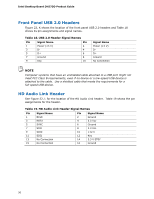
Installing and Replacing Desktop Board Components S/PDIF Header Figure 22, C shows the location of the S/PDIF output header. Table 10 shows the pin assignments and signal names for the S/PDIF output header. Table 10. S/PDIF Header Signal Names Pin Description 1 Ground 2 S/PDIF Out 3 Key (no pin) 4 +5 VDC Serial Header Figure 22, D shows the location of the serial header. Table 11 shows the pin assignments and signal names for the serial header. Table 11. Serial Port Header Pin Signal Name 1 DCD (Data Carrier Detect) 3 TXD# (Transmit Data) 5 Ground 7 RTS (Request To Send) 9 RI (Ring Indicator) Pin Signal Name 2 RXD# (Receive Data) 4 DTR (Data Terminal Ready) 6 DSR (Data Set Ready) 8 CTS (Clear To Send) 10 Key (no pin) Consumer IR (CIR) Headers The Desktop Board has two CIR headers: the receiver or input header (Figure 22, F) and the output or emitter header (Figure 22, E). The receiver header consists of a filtered translated infrared input compliant with Microsoft CIR specifications and a "learning" infrared input. The learning input is a high-pass input which the computer can use to "learn" to speak the infrared communication language of other user remotes. The emitter header consists of two output ports which the computer can use to emulate "learned" infrared commands in order to control external electronic hardware. NOTE The Consumer IR option must be enabled in the system BIOS before it can function. Press at boot to enter the system BIOS, and go to Advanced > Peripheral Configuration > Enhanced Consumer IR, and set this option to Enabled. 47