Intermec CV30 Intermec Terminal Emulator (ITE) User Guide - Page 44
Using a Configuration File for SSH Settings, Locking Down SSH Applications, SSH Option Descriptions
 |
View all Intermec CV30 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 44 highlights
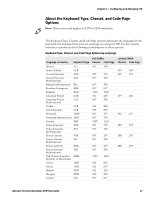
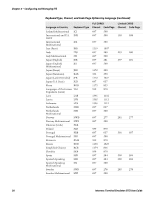
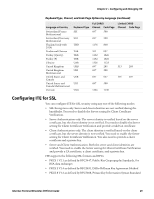
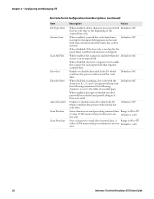
Chapter 2 - Configuring and Managing ITE SSH Option Descriptions Option SSH UserName SSH PassWord SSH Private Key SSH Key Passphrase Receive LF as CRLF Description Stored username you are prompted to enter when you choose to connect to Port 22 (SSH) instead of Port 23 (Telnet). Stored password you are prompted to enter when you choose to connect to Port 22 (SSH) instead of Port 23 (Telnet). Key file SSH uses for private key authentication. Specify the relative path from \Program Files \Intermec\ITE\SSH\, or prefix the absolute path with \. Passphrase required to access the SSH Private Key file. If blank, ITE assumes no passphrase was configured. When enabled, when ITE receives a line feed from the host, it is treated as a carriage return + line feed. This is required for proper formatting of some Linux connections, but must be disabled for correct display of some Windows-based server screens. Values 0 to 80 characters. Default is a null string. 0 to 80 characters. Default is a null string. 0 to 80 characters. Default is a null string. 0 to 80 characters. Default is a null string. Enabled or Disabled. Default is Enabled. Using a Configuration File for SSH Settings The ITE implementation of the OpenSSH client provides for additional configuration options and settings. To configure these settings, use the Open SSH configuration file located in: • \Program Files\Intermec\ITE\SSH (all computers except CV41 running Windows CE) • \System\ITEdata\ssh (CV41 running Windows CE only) If you use the configuration file, settings made in ITE (such as port number and host name) override the settings in the file. A complete description of Open SSH options and settings is beyond the scope of this manual. For more information on Open SSH client configuration options and settings, see http://www.manpagez.com/man/5/ssh_config/. Note: ITE supports public key authentication for Open SSH. This feature is configured from within ITE and not through the configuration file. Locking Down SSH Applications To prevent a user from getting to the command prompt, a telnet server can bring itself up during startup (as part of the standard services). Logging into the SSH server as a shell brings up the command prompt. On a Linux system, you can prevent this by creating a login script that executes your host application and then posts "exit" as its last command. Specifically, in the user account .pro file, append the following lines: trap 2 ./ pgmName exit 32 Intermec Terminal Emulator (ITE) User Guide