JVC G300 Instruction Manual - Page 17
Mp3 Introduction
 |
UPC - 046838008214
View all JVC G300 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 17 highlights
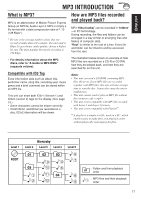
ENGLISH MP3 INTRODUCTION What is MP3? MP3 is an abbreviation of Motion Picture Experts Group (or MPEG) Audio Layer 3. MP3 is simply a file format with a data compression ratio of 1:10 (128 Kbps*). * Bit rate is the average number of bits that one second of audio data will consume. The unit used is Kbps. To get a better audio quality, choose a higher bit rate. The most popular bit rate for encoding is 128 Kbps. • For details information about the MP3 discs, refer to "A Guide to MP3/WMA" (separate volume). Compatible with ID3 Tag Extra information data such as album title, performer name, song title, recording year, music genre and a brief comment can be stored within an MP3 file. This unit can show both ID3v1 (Version 1) and ID3v2 (version 2) tags on the display. (See page 19.) • Some characters cannot be shown correctly. • If both ID3v1 and ID3v2 are recorded on a disc, ID3v2 information will be shown. How are MP3 files recorded and played back? MP3 "files (tracks)" can be recorded in "folders" -in PC terminology. During recording, the files and folders can be arranged in a way similar to arranging files and folders of computer data. "Root" is similar to the root of a tree. Every file and folder can be linked to and be accessed from the root. The illustration below shows an example of how MP3 files are recorded on a CD-R or CD-RW, how they are played back, and how they are searched for on this unit. Notes: • This unit can read a CD-ROM containing MP3 files. However, if non-MP3 files are recorded together with MP3 files, this unit will take a longer time to scan the disc. It may also cause the unit to malfunction. • This unit cannot read or play an MP3 file without the extension code . • This unit is not compatible with MP3 file encoded with Layer 1 and Layer 2 formats. • This unit is not compatible with Playlist**. ** A playlist is a simple text file, used on a PC, which enables users to make their own playback order without physically rearranging the files. Level 1 ROOT Hierarchy Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 01 02 03 6 3 4 7 05 10 5 1 11 04 8 2 12 9 : Folder and their playback 01 order : MP3 files and their playback 1 order 17