LG GR-K192AF Service Manual - Page 49
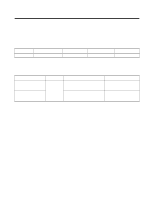
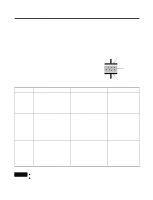
Current, Main pole, Removal of magnetic velocity, on the pole surface
 |
View all LG GR-K192AF manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 49 highlights
Characteristics of each part • Operating principle When the AD power is connected to the coil of the shading pole motor, the central axis of the magnetic field shifts in the bold arrow direction of . As the central axis moves, the rotor moves in the same direction to turn the motor. Why does the central axis of the magnetic field shift? shows a diagram of AC current changing as time changes. If you look at changes of magnetic velocity in "a' zone where the current abruptly increases, the velocity increases as the current increases in the main pole. But in the shading pole, the negative effect of the velocity increase is generated from the shading coil to reduce the velocity shifting the center of the magnetic field to the main pole. In "b" zone, the change in current is minimal and the negative effect of shading coil is minimal to have the center of the magnetic field in the middle as shown in . In "c" zone, the velocity of the main pole decreases but with the negative effect increasing the velocity from the shading pole side, the center shifts to the shading pole side. As shown, the center of the magnetic field shifts from the main pole to the shading pole to rotate the rotor. Current ab c Time Change of AC current Main pole Shading Pole "a" zone "b" zone "c" zone Removal of magnetic velocity on the pole surface Change in magnetic velocity by changes in current - 49 -