Lenovo PC 300PL Technical Information Manual 6562, 6592 - Page 46
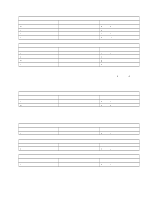
Hardware Interrupts
 |
View all Lenovo PC 300PL manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 46 highlights
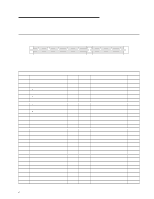
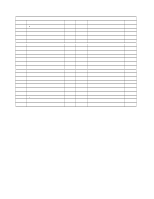
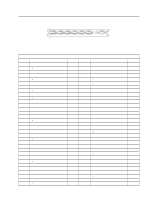
Chapter 6. System Compatibility Hardware Interrupts Hardware interrupts are level-sensitive for PCI interrupts and edge-sensitive for ISA interrupts. The interrupt controller clears its in-service register bit when the interrupt routine sends an End of Interrupt (EOI) command to the controller. The EOI command is sent regardless of whether the incoming interrupt request to the controller is active or inactive. The interrupt-in-progress latch is readable at an I/O-address bit position. This latch is read during the interrupt service routine and might be reset by the read operation, or it might require an explicit reset. Note: For performance and latency considerations, designers might want to limit the number of devices sharing an interrupt level. With level-sensitive interrupts, the interrupt controller requires that the interrupt request be inactive at the time the EOI command is sent; otherwise, a new interrupt request will be detected. To avoid this, a level-sensitive interrupt handler must clear the interrupt condition (usually by a read or write operation to an I/O port on the device causing the interrupt). After processing the interrupt, the interrupt handler: 1. Clears the interrupt 2. Waits one I/O delay 3. Sends the EOI 4. Waits one I/O delay 5. Enables the interrupt through the Set Interrupt Enable Flag command Hardware interrupt IRQ9 is defined as the replacement interrupt level for the cascade level IRQ2. Program interrupt sharing is implemented on IRQ2, interrupt 0Ah. The following processing occurs to maintain compatibility with the IRQ2 used by IBM Personal Computer products: 1. A device drives the interrupt request active on IRQ2 of the channel. 2. This interrupt request is mapped in hardware to IRQ9 input on the second interrupt controller. 3. When the interrupt occurs, the system microprocessor passes control to the IRQ9 (interrupt 71h) interrupt handler. 4. This interrupt handler performs an EOI command to the second interrupt controller and passes control to the IRQ2 (interrupt 0Ah) interrupt handler. 5. This IRQ2 interrupt handler, when handling the interrupt, causes the device to reset the interrupt request before performing an EOI command to the master interrupt controller that finishes servicing the IRQ2 request. 34 Technical Information Manual