Lenovo ThinkPad Edge S230u (English) Password Manager 4 Deployment Guide - Page 13
Active Directory support, Defining manageable settings - specification
 |
View all Lenovo ThinkPad Edge S230u manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 13 highlights
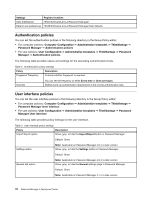
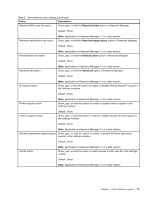
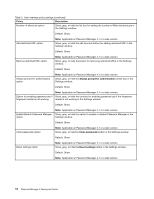
Chapter 4. Active Directory support The ADM (Administrative) template file defines policy settings used by applications on client computers. Policies are specific settings that govern the application behavior. Policy settings also define whether the user will be allowed to set specific settings through the application. Settings defined by an administrator on the server are defined as policies. Settings defined by a user on the client computer for an application are defined as preferences. As defined by Microsoft, policy settings take precedence over preferences. For example, a user might put a background image on the desktop. This is a user preference. An administrator might define a setting on the server dictating that a user must use a specific background image. The administrator's policy setting overrides the user preference. When a ThinkVantage program checks for a setting, it looks for the setting in the following order: • Computer policies • User policies • Default user policies • Computer preferences • User preferences • Default user preferences As described previously, all policies, including computer policies and user policies, are defined by the administrator. These settings can be initialized through the XML configuration file or through a Group Policy in Active Directory. Computer and user preferences are set by the user on the client computer through options in the application interface. Default user preferences are initialized by the XML configuration script. Users do not change the values directly. Changes made to these settings by a user will be updated in the user preferences. Customers not using Active Directory can create a default set of policy settings to be deployed to client computers. Administrators can modify XML configuration scripts and specify that they be processed during the installation of the program. Defining manageable settings You can set the Password Manager policies in the Group Policy editor. The following example shows the location where you can find the Fingerprint Frequency option in the Group Policy editor. Example: Computer Configuration ➙ Administrative Templates ➙ ThinkVantage ➙ Password Manager ➙ Authentication Policies ➙ Fingerprint Frequency The ADM files indicate where in the registry the settings will be reflected. These settings will be in the following registry locations: Settings Computer policies User policies Default user policies Computer preferences Registry locations HKLM\Software\Policies\Lenovo\Password Manager\ HKCU\Software\Policies\Lenovo\Password Manager\ HKLM\Software\Policies\Lenovo\Password Manager\User defaults HKLM\Software\Lenovo\Password Manager\ © Copyright Lenovo 2012 9