MSI 915G COMBO-FR User Manual - Page 18
Memory, Introduction to DDR2 & DDR1 SDRAM - power supply
 |
UPC - 816909005905
View all MSI 915G COMBO-FR manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 18 highlights
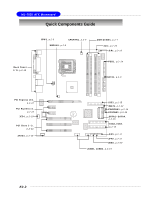
Hardware Setup Memory The mainboard provides 2 slots for 184-pin DDR1 DIMM (Double In-Line Memory Module) modules and 2 slots for 240-pin DDR2 DIMM, which supports the memory size up to 2GB. Since DDR2 modules are not interchangeable with DDR1 and the DDR2 standard is not backward compatible, you should always install DDR2 memory module in DDR2 slot (DIMM1 & DIMM3), and DDR1 memory module in DDR1 slot (DIMM2 & DIMM4). Wrong installation may cause damage of mainboard. Meanwhile, you are not able to boot up your system if you install DDR1 & DDR2 memory modules simultaneously. For the updated supporting memory modules, please visit http://www.msi. com.tw/program/products/mainboard/mbd/pro_mbd_trp_list.php. DIMM1~DIMM4 (from left to right) DIMM1 & DIMM3 are for DDR2 memory module DIMM2 & DIMM4 are for DDR1 memory module Introduction to DDR2 & DDR1 SDRAM DDR2 is a new technology of memory module, and its speed is the top limit of current DDR1 technology. DDR2 uses a 1.8V supply for core and I/O voltage, compared to 2.5V for DDR1, and requires 28% less power than DDR1 chips. DDR2 truly is the future of memory, but will require some changes as the technology is not backwardly compatible and only motherboards specifically designed for DDR2 memory will be able to support these chips. DDR2 incorporates new features at the chip level that give it better signal integrity, thereby enabling higher clock speeds. DDR2 modules have 240 pins, versus 184 pins on a DDR1 module, and the length of DDR2 module is 5.25". DDR2 modules have smaller and tighter spaced pins. The height of DDR2 modules varies, but they will typically be less than 1.3" in height. DDR1 SDRAM is similar to conventional SDRAM, but doubles the rate by transferring data twice per cycle. It uses 2.5 volts, and requires 184-pin DIMM modules. E2-7